COVID-19 has impacted the way many people go about their daily lives, but what are the main factors driving the changes in the housing market, particular house prices?
Read More...Browse Articles
Modelling effects of alkylamines on sea salt aerosols using the Extended Aerosols and Inorganics Model

With monitoring of climate change and the evolving properties of the atmosphere more critical than ever, the authors of this study take sea salt aerosols into consideration. These sea salt aerosols, sourced from the bubbles found at the surface of the sea, serve as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and are effective for the formation of clouds, light scattering in the atmosphere, and cooling of the climate. With amines being involved in the process of CCN formation, the authors explore the effects of alkylamines on the properties of sea salt aerosols and their potential relevance to climate change.
Read More...Comparing the Effectiveness of Popular Treatments for Swelling and Scarring
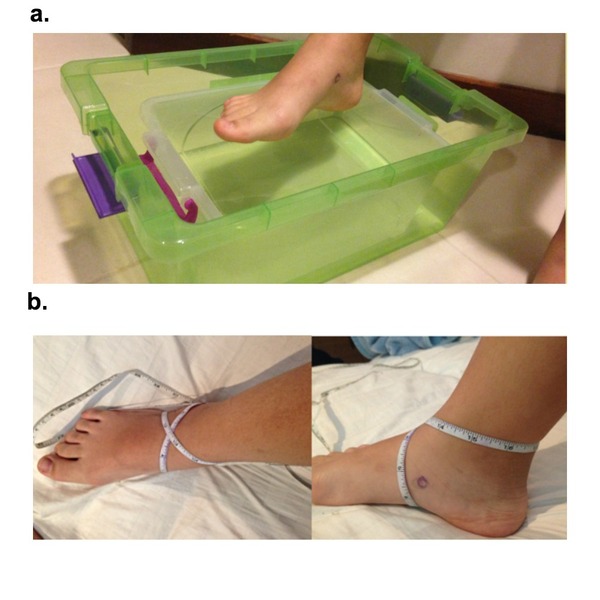
Numerous specialty treatments claim to reduce swelling and scarring; however, it is unknown if these treatments are more effective than less expensive treatments. In an attempt to determine if one outperforms the other, treatments were applied to the same subject following bilateral orthopedic foot surgery. No difference was found the specialty treatments compared to more cost-effective treatments.
Read More...Practical applications of the Fourier analysis to identify pitches and synthesize sounds in music
In this study the authors looked at the ability of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to analyze different musical elements. They found that DFT is a powerful method to analyze recorded music.
Read More...Surface cleanliness of hydrothermally grown zinc oxide microparticles compared to commercial nanoparticles

The authors test the usefulness of zinc oxide microparticles relative to zinc oxide nanoparticles as antibacterial agents.
Read More...Factors Influencing Muon Flux and Lifetime: An Experimental Analysis Using Cosmic Ray Detectors
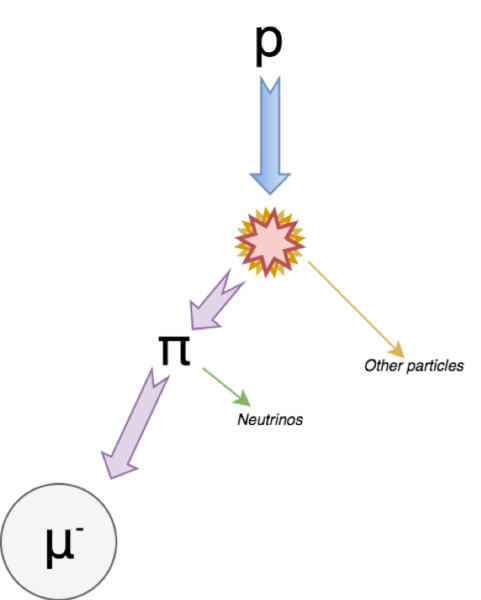
Muons, one of the fundamental elementary particles, originate from the collision of cosmic rays with atmospheric particles and are also generated in particle accelerator collisions. In this study, Samson et al analyze the factors that influence muon flux and lifetime using Cosmic Ray Muon Detectors (CRMDs). Overall, the study suggests that water can be used to decrease muon flux and that scintillator orientation is a potential determinant of the volume of data collected in muon decay studies.
Read More...