
In this article, the authors identify the characteristics that make a book a best-seller. Knowing what, besides content, predicts the success of a book can help publishers maximize the success of their print products.
Read More...A Novel Model to Predict a Book's Success in the New York Times Best Sellers List

In this article, the authors identify the characteristics that make a book a best-seller. Knowing what, besides content, predicts the success of a book can help publishers maximize the success of their print products.
Read More...Comparison of spectral subtraction noise reduction algorithms

Here, the authors investigated methods to reduce noise in audio composed of real-word sounds. They specifically used two spectral subtraction noise reduction algorithms: stationary and non-stationary finding notable differences in noise improvements depending on the noise sources.
Read More...Association between nonpharmacological interventions and dementia: A retrospective cohort study

Here, the authors investigated the role of nonpharmacological interventions in preventing or delaying cognitive impairment in individuals with and without dementia. By using a retrospective case-control study of 22 participants across two senior centers in San Diego, they found no significant differences in self-reported activities. However, they found that their results reflected activity rather than the activity itself, suggesting the need for an alternative type of study.
Read More...Impact of study partner status and group membership on commitment device effectiveness among college students

Here seeking to identify a possible solution to procrastination among college students, the authors used an online experiment that involved the random assignment of study partners that they shared their study time goal with. These partners were classified by status and group membership. The authors found that status and group membership did not significantly affect the likelihood of college students achieving their committed goals, and also suggest the potential of soft commitment devices that take advantage of social relationships to reduce procrastination.
Read More...Analysis of Patterns in the Harmonics of a String with Artificially Enforced Nodes
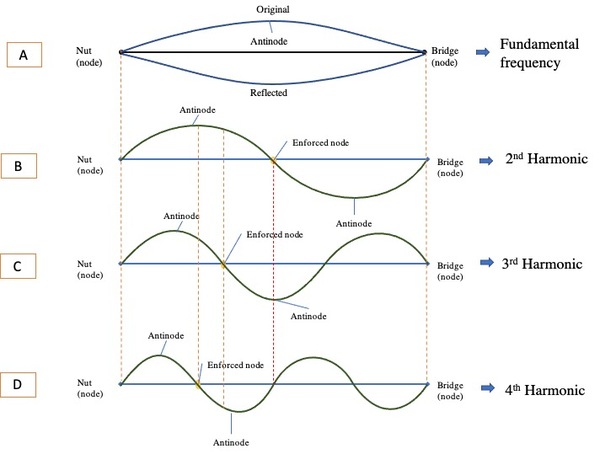
This study examines the higher harmonics in an oscillating string by analyzing the sound produced by a guitar with a spectrum analyzer. The authors mathematically hypothesized that the higher harmonics in the series of the directly excited 2nd harmonic contain the alternate frequencies of the fundamental series, the higher harmonics of the directly excited 3rd harmonic series contain every third frequency of fundamental series, and so on. To test the hypotheses, they enforced artificial nodes to excite the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th harmonics directly, and analyzed the resulting spectrum to verify the mathematical hypothesis. The data analysis corroborates both hypotheses.
Read More...Rhythmic lyrics translation: Customizing a pre-trained language model using stacked fine-tuning

Neural machine translation (NMT) is a software that uses neural network techniques to translate text from one language to another. However, one of the most famous NMT models—Google Translate—failed to give an accurate English translation of a famous Korean nursery rhyme, "Airplane" (비행기). The authors fine-tuned a pre-trained model first with a dataset from the lyrics domain, and then with a smaller dataset containing the rhythmical properties, to teach the model to translate rhythmically accurate lyrics. This stacked fine-tuning method resulted in an NMT model that could maintain the rhythmical characteristics of lyrics during translation while single fine-tuned models failed to do so.
Read More...Open string vibrato: does it exist?
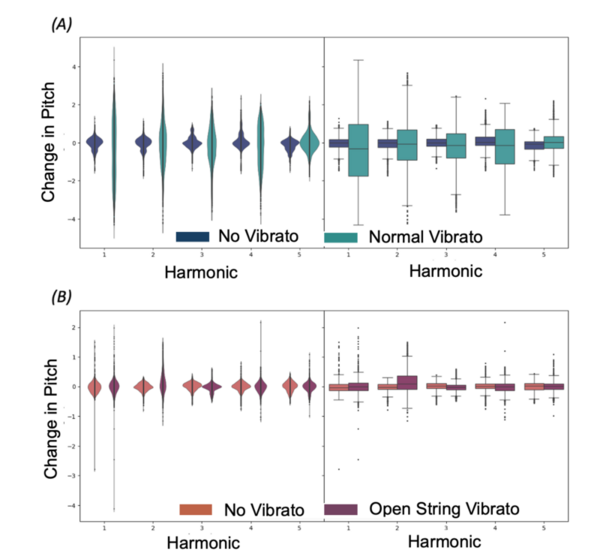
Vibrato, defined as a rapid and subtle oscillation in pitch, is a technique that is commonly used by musicians to add expression and colour to notes. However, on stringed instruments, there are certain notes (open string notes) on which it is impossible to perform the technique. Without vibrato, they can sound angular and unpleasant, especially when juxtaposed against other notes played with vibrato. String players therefore use an alternative to achieve the same vibrato effect on the open string — a technique referred to as “open string vibrato”. While the technique is widely used, it is unknown how much of a physical effect it has on the sound waves produced, if any at all. The purpose of this study is to analyse open string vibrato using a statistical approach to provide evidence to characterize the physical effect of the technique, and then compare it to normal vibrato. We hypothesised that it would have a noticeable and measurable effect on the sound waves produced because of the technique’s widespread usage. To test this, notes, with and without either open string vibrato or normal vibrato, were recorded on the violin. We analyzed the audio recordings using a computational and statistical approach. The results of the study partially agreed with our hypothesis: while the technique has an observable physical effect on the sound waves, the effect is weaker than expected. We concluded that open string vibrato does work, but has quite a subtle effect, and thus should only be used when there is no other option.
Read More...