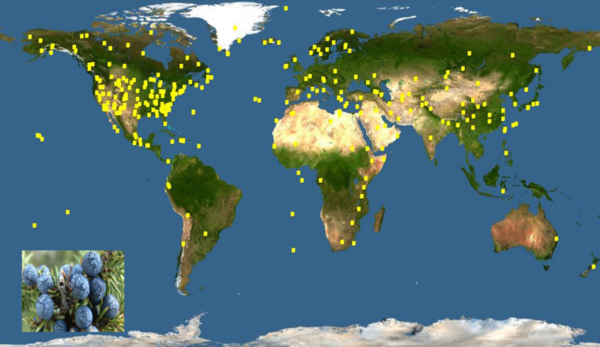
Many species of trees are distributed widely around the world, though not always in a way that makes immediate sense. The authors here use genetic information to help explain the geographic distribution of various conifer species throughout the world.
Read More...
.jpg)
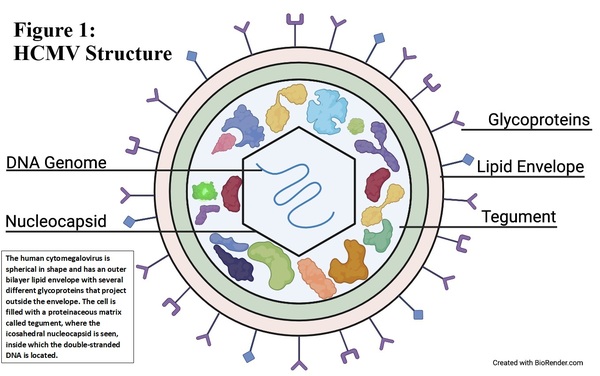
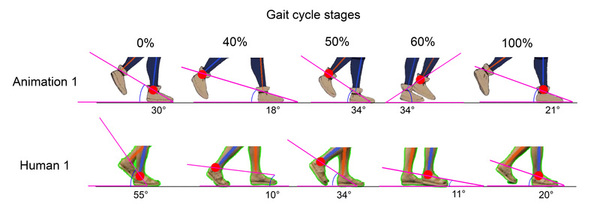
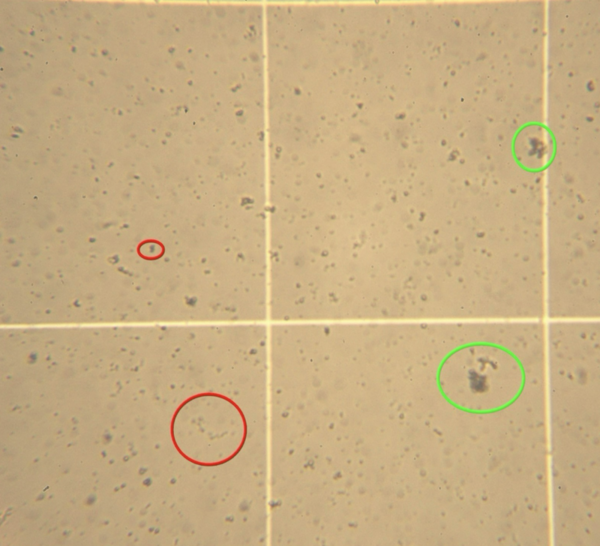

.png)