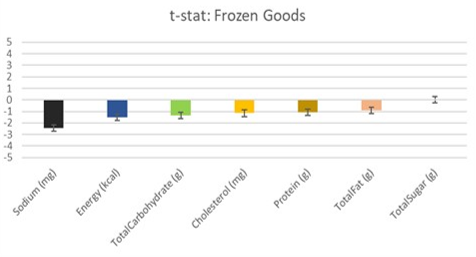
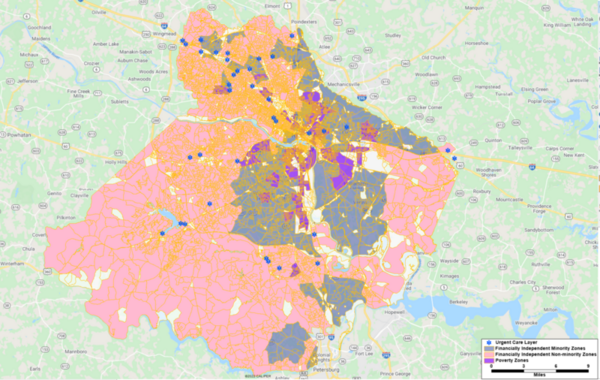
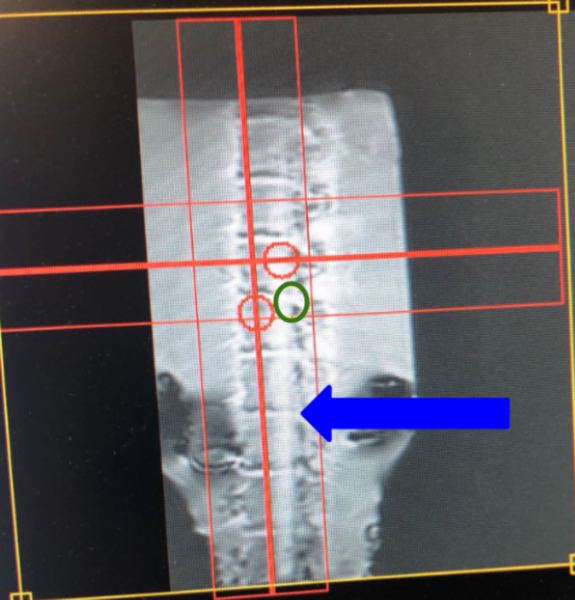
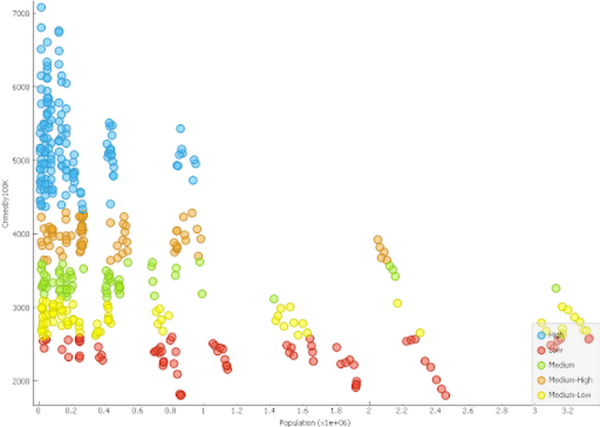
In our work we followed the formation of gas bubbles on the surface of the vessel walls in different carbonated liquids, over different time intervals, at different temperatures and in vessels made of different materials. Our results made it possible to identify patterns affecting the process of formation and disappearance of carbon dioxide bubbles.
Read More...