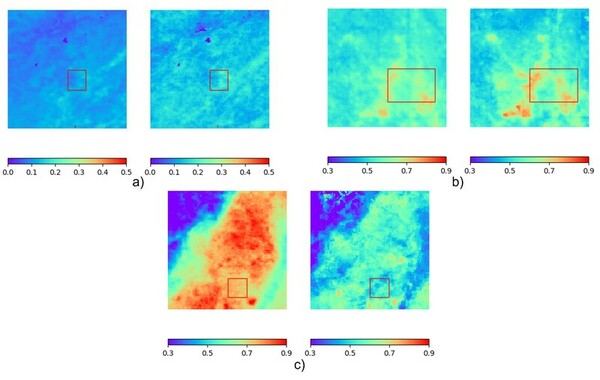
In this study, the authors use aerosol optical depth data to determine if aerosol levels were lower in major metropolitan areas around the world during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read More...Analyzing aerosol variation during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown using satellite data

In this study, the authors use aerosol optical depth data to determine if aerosol levels were lower in major metropolitan areas around the world during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read More...A comparative analysis of synthetic and natural fabrics
The authors test the durability of synthetic versus non-synthetic fabrics though loose thread counts, color fade over time, and shrinkage tests.
Read More...Evaluating machine learning algorithms to classify forest tree species through satellite imagery

Here, seeking to identify an optimal method to classify tree species through remote sensing, the authors used a few machine learning algorithms to classify forest tree species through multispectral satellite imagery. They found the Random Forest algorithm to most accurately classify tree species, with the potential to improve model training and inference based on the inclusion of other tree properties.
Read More...Exponential regression analysis of the Canadian Zero Emission Vehicle market’s effects on climate emissions in 2030

Here, the authors explored how the sale and use of electric vehicles could reduce emissions from the transport industry in Canada. By fitting the sale of total of electric vehicles with an exponential model, the authors predicted the number of electric vehicle sales through 2030 and related that to the average emission for such vehicles. Ultimately, they found that the sale and use of electric vehicles alone would likely not meet the 45% reduction in emissions from the transport industry suggested by the Canadian government
Read More...An accessible experiment to assess the impact of shapes of buildings and roofs on wind resistance
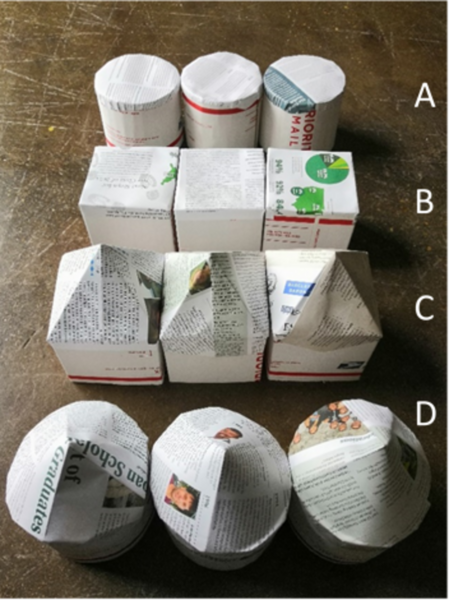

In this study, the authors determine which house model is most resistant to high winds by building smaller prototypes that could be tested with a handheld source of wind.
Read More...Managing CO2 levels through precipitation-based capture from seawater and electrochemical conversion
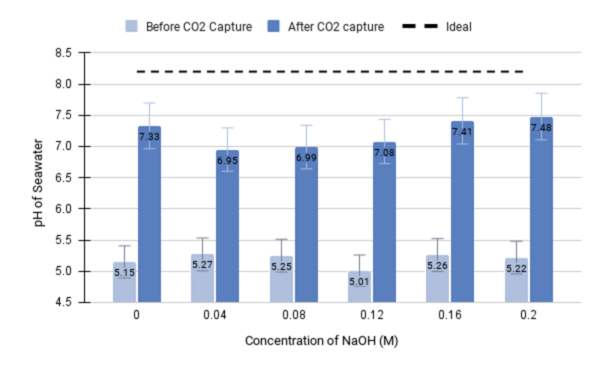
The authors set out to develop an electrochemical device that would have efficient and sustained carbon dioxide capture.
Read More...Survival of Escherichia coli K-12 in various types of drinking water

For public health, drinking water should be free of bacterial contamination. The objective of this research is to identify the fate of bacteria if drinking water becomes contaminated and inform consumers on which water type enables the least bacteria to survive. We hypothesized that bottled mineral water would provide the most sufficient conditions for E. coli to survive. We found that if water becomes contaminated, the conditions offered by the three water types at room temperature allow E. coli to survive up to three days. At 72 hours, the bottled spring water had the highest average colony forming units (CFUs), with tap and mineral water CFU values statistically lower than spring water but not significantly different from each other. The findings of this research highlight the need of implementing accessible quality drinking water for the underserved population and for the regulation of water sources.
Read More...Effects of polyethylene microplastics on the growth of Arabidopsis thaliana & Phaseolus vulgaris and their soil
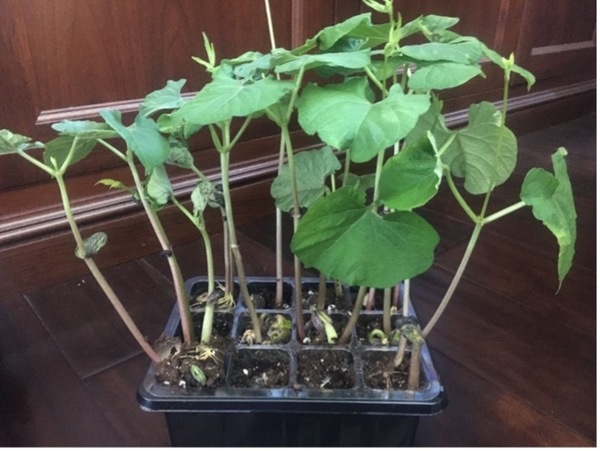

In this study, the authors investigate whether microplastics affect terrestrial plant growth and soil quality.
Read More...The role minor and major snowfall events play in New Jersey snowfall over the past 126 years

Climate records indicate that there has been a trend of decreasing annual snowfall totals throughout the United States during the peak winter season. However, New Jersey has seen a significant increase in snowfall over the past 126 years of recorded observations. The authors hypothesize that although annual snowfall has remained the same on average, the frequencies of major and minor snowfall events have noticeably increased. They found that there was no significant evidence for an increase in the frequency of minor events (1.1-inch to 4.0-inch events), but there was evidence for an increase in the frequency of major events (4.1+ inch events). The results imply that a warming climate might be opening up opportunities for more snowfall.
Read More...A potentially underestimated source of CO2 and other greenhouse gases in agriculture

Here the authors investigated the role of agricultural fertilizers as potential contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast to the typical investigations that consider microbiological processes, the authors considered purely chemical processes. Based on their results they found that as much as 20.41% of all CO2 emission from land-based activities could be a result of mineral nitrogen fertilizers.
Read More...