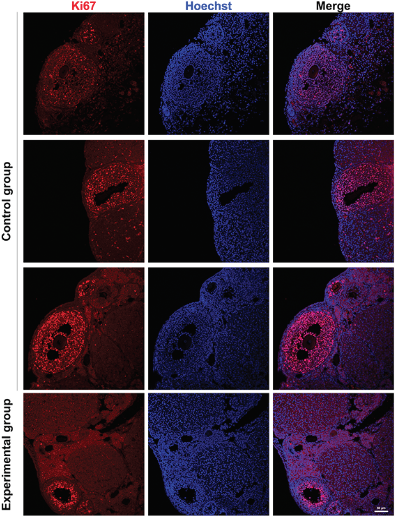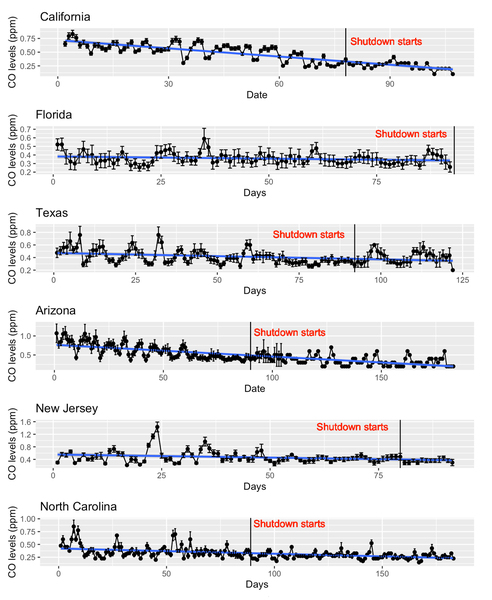
Concerns regarding the rapid spread of Sars-CoV2 in early 2020 led company and local governmental officials in many states to ask people to work from home and avoid leaving their homes; measures commonly referred to as shutdowns. Here, the authors investigate how shutdowns affected carbon monoxide (CO) levels in 15 US states using publicly available data. Their results suggest that CO levels decreased as a result of these measures over the course of 2020, a trend which started to reverse after shutdowns ended.
Read More...