
The authors studied the impact of AI face-tracking technology on the immersiveness of videogames as an alternative to virtual reality gaming.
Read More...Artificial intelligence face-tracking for a semi-virtual reality gaming experience

The authors studied the impact of AI face-tracking technology on the immersiveness of videogames as an alternative to virtual reality gaming.
Read More...Efficacy of Mass Spectrometry Versus 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance With Respect to Denaturant Dependent Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange in Protein Studies
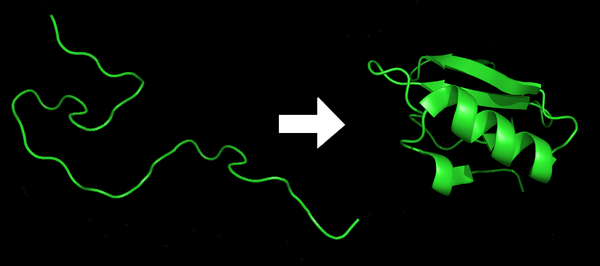
The misfolding of proteins leads to numerous diseases including Akzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Type II Diabetes. Understanding of exactly how proteins fold is crucial for many medical advancements. Chenna and Englander addressed this problem by measuring the rate of hydrogen-deuterium exchange within proteins exposed to deuterium oxide in order to further elucidate the process of protein folding. Here, mass spectrometry was used to measure exchange in Cytochrome c and was compared to archived 1H NMR data.
Read More...Practical applications of the Fourier analysis to identify pitches and synthesize sounds in music
In this study the authors looked at the ability of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to analyze different musical elements. They found that DFT is a powerful method to analyze recorded music.
Read More...Analyzing breath sounds by using deep learning in diagnosing bronchial blockages with artificial lung
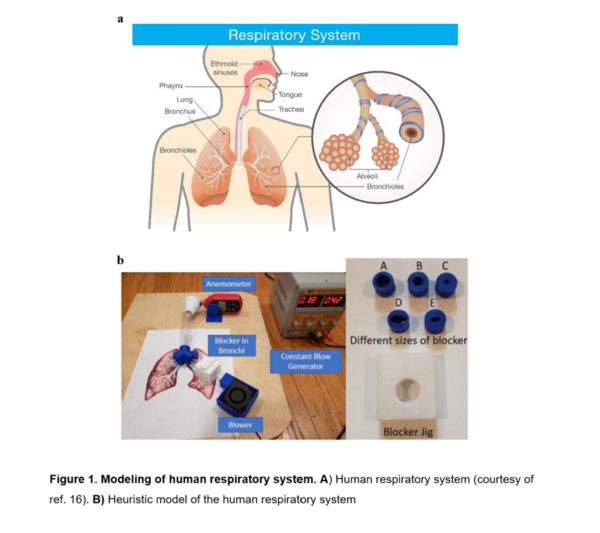
Many common respiratory illnesses like bronchitis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) lead to bronchial inflammation and, subsequently, a blockage. However, there are many difficulties in measuring the severity of the blockage. A numeric metric to determine the degree of the blockage severity is necessary. To tackle this demand, we aimed to develop a novel human respiratory model and design a deep-learning program that can constantly monitor and report bronchial blockage by recording breath sounds in a non-intrusive way.
Read More...Using neural networks to detect and categorize sounds
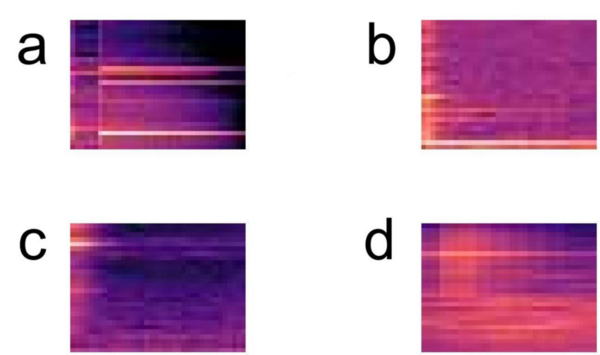
The authors test different machine learning algorithms to remove background noise from audio to help people with hearing loss differentiate between important sounds and distracting noise.
Read More...The impact of environmental noise on the cognitive functions and mental workload of high school students
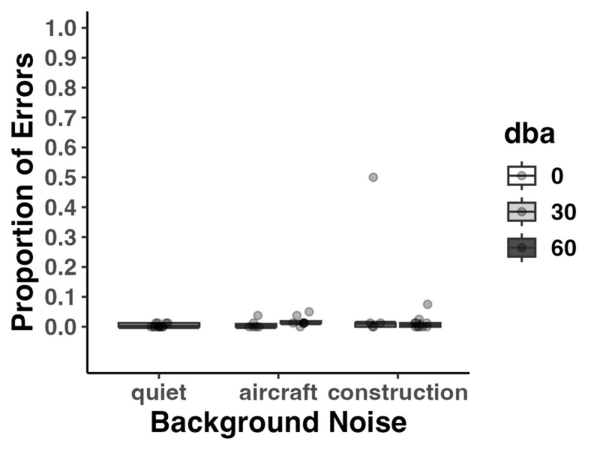
Authors examine the impact of environmental noise on cognitive processes in teenagers, focusing on five different noise conditions: two types of noise (aircraft and construction) at two different decibel levels (30 dBA and 60 dBA) and a quiet condition.
Read More...Comparison of spectral subtraction noise reduction algorithms

Here, the authors investigated methods to reduce noise in audio composed of real-word sounds. They specifically used two spectral subtraction noise reduction algorithms: stationary and non-stationary finding notable differences in noise improvements depending on the noise sources.
Read More...Optimizing data augmentation to improve machine learning accuracy on endemic frog calls
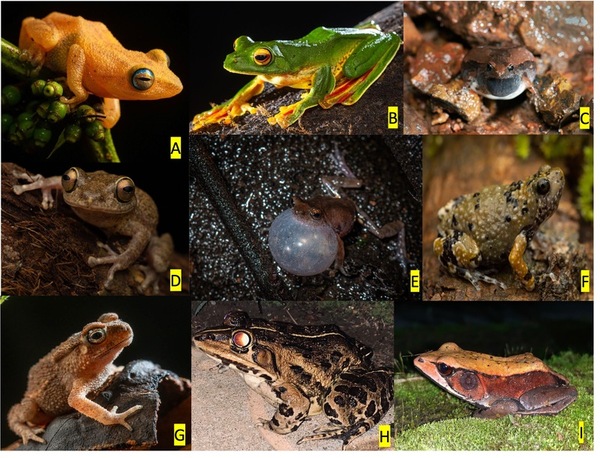

The mountain chain of the Western Ghats on the Indian peninsula, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is home to about 200 frog species, 89 of which are endemic. Distinctive to each frog species, their vocalizations can be used for species recognition. Manually surveying frogs at night during the rain in elephant and big cat forests is difficult, so being able to autonomously record ambient soundscapes and identify species is essential. An effective machine learning (ML) species classifier requires substantial training data from this area. The goal of this study was to assess data augmentation techniques on a dataset of frog vocalizations from this region, which has a minimal number of audio recordings per species. Consequently, enhancing an ML model’s performance with limited data is necessary. We analyzed the effects of four data augmentation techniques (Time Shifting, Noise Injection, Spectral Augmentation, and Test-Time Augmentation) individually and their combined effect on the frog vocalization data and the public environmental sounds dataset (ESC-50). The effect of combined data augmentation techniques improved the model's relative accuracy as the size of the dataset decreased. The combination of all four techniques improved the ML model’s classification accuracy on the frog calls dataset by 94%. This study established a data augmentation approach to maximize the classification accuracy with sparse data of frog call recordings, thereby creating a possibility to build a real-world automated field frog species identifier system. Such a system can significantly help in the conservation of frog species in this vital biodiversity hotspot.
Read More...The influence of working memory on auditory category learning in the presence of visual stimuli

Here in an effort to better understand how our brains process and remember different categories of information, the authors assessed working memory capacity using an operation span task. They found that individuals with higher working memory capacity had higher overall higher task accuracy regardless of the type of category or the type of visual distractors they had to process. They suggest this may play a role in how some students may be less affected by distracting stimuli compared to others.
Read More...