
The authors use machine learning to develop an evidence-based detection tool for identifying human trafficking.
Read More...Uncovering the hidden trafficking trade with geographic data and natural language processing

The authors use machine learning to develop an evidence-based detection tool for identifying human trafficking.
Read More...A juxtaposition of the effects of natural and chemical fertilizers on Ocimum basilicum
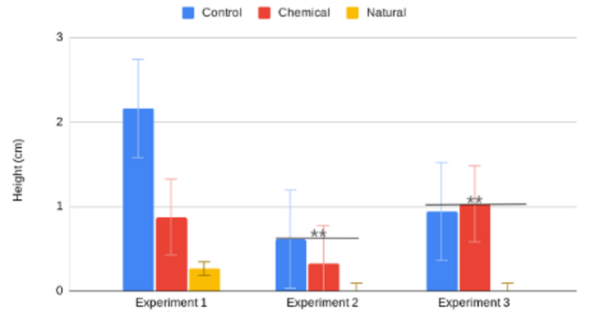
Agricultural fertilizer application is a key innovation in providing enough food to feed the world. Fertilizers come in various types and farmers must choose which fertilizer is the best for their applications. To learn more about the effectiveness of various fertilizers, Wilson and Rasmus studied the effects of natural and chemical fertilizers on growth of basil plants.
Read More...A novel filtration model for microplastics using natural oils and its application to the environment
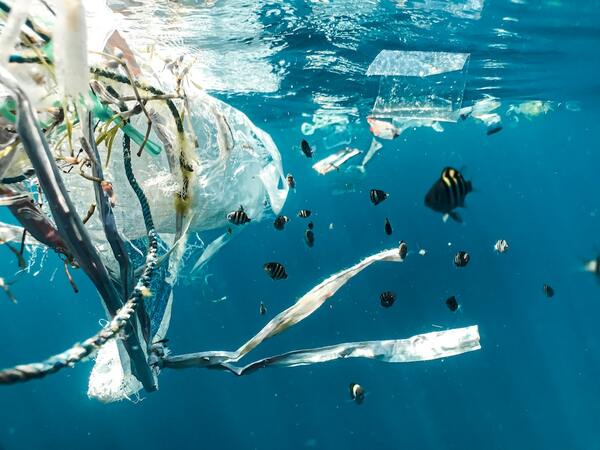

Recognizing the need for a method to filter microplastics from polluted water the authors sought to use nonpolar solvents, palm oil and palm kernel oil, to filter microplastics out of model seawater. By relying on the separation of polar and nonpolar solvents followed by freezing the nonpolar solvent, they reported that microplastics could be extracted with percentages ranging from 96.2% to 94.2%. They also provided an estimation to use this method as part of container ships to clean the Pacific Ocean of microplastics.
Read More...Virtual Screening of Cutibacterium acnes Antibacterial Agent Using Natural Compounds Database
A common form of Acne is caused by a species of bacterium called Cutibacterium acnes. By using a predictive algorithm and structural analysis, the authors identified 5 small molecules with high affinity to growth factors in Catibacterium acnes. This has potential implications for supplemental skincare products.
Read More...Developing a Method to Remove Inorganic Arsenic from Rice with Natural Substances
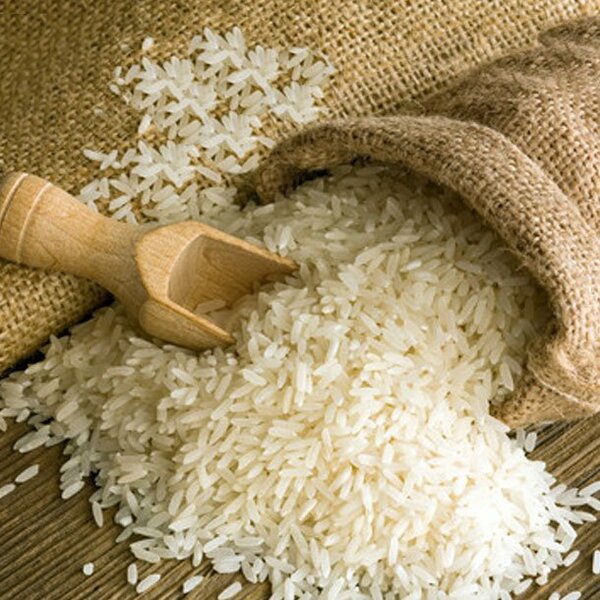

In this study, the authors tested different approaches for removing arsenic from rice. Due to higher arsenic levels in water, some areas grow rice with higher levels as well. This is a health hazard and so developing methods to remove arsenic from the rice will be helpful to many. Using a rapid arsenic kit, the authors found that activated charcoal was the most effective at removing arsenic from rice.
Read More...Allelopathic Effects of Kudzu (Pueraria montana) on Seed Germination and Their Potential Use As a Natural Herbicide
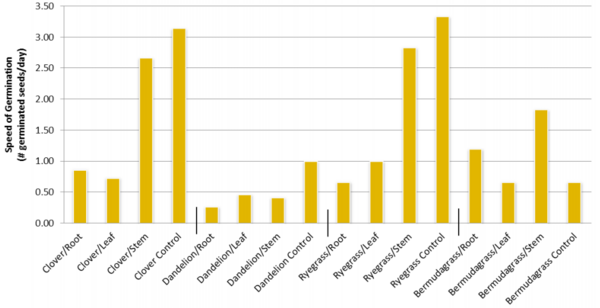
Plants in the wild compete with each other for nutrients and sunlight. Kudzu is a weed that is thought to secrete compounds that inhibit the growth of other plants. Here the authors find that certain parts of kudzu plants can block the germination of clover and dandelion seeds. These experiments may lead to a weed killer that is safe and naturally derived.
Read More...A Novel Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutic Model: Attenuating Hyperphosphorylated Tau and Amyloid β (Aβ) Aggregates by Characterizing Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Neuroprotective Properties of Natural Extracts
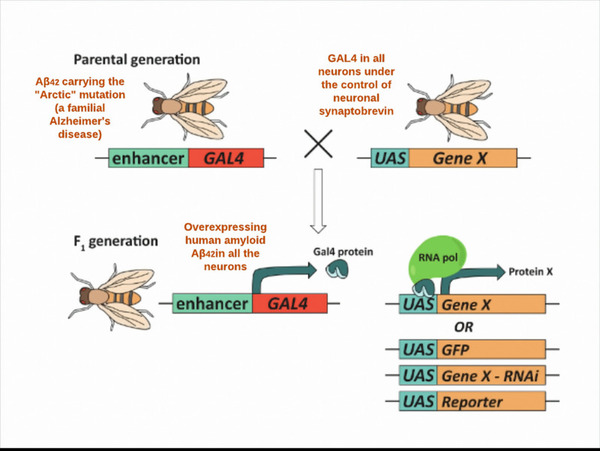
Oxidative damage and neuro-inflammation were the key pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. In this study, 30 natural extracts from plant roots and leaves with extensive anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties were consumed by Drosophila melanogaster. Several assays were performed to evaluate the efficacy of these combinational extracts on delaying the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. The experimental group showed increased motor activity, improved associative memory, and decreased lifespan decline relative to the control group.
Read More...Gradient boosting with temporal feature extraction for modeling keystroke log data
Although there has been great progress in the field of Natural language processing (NLP) over the last few years, particularly with the development of attention-based models, less research has contributed towards modeling keystroke log data. State of the art methods handle textual data directly and while this has produced excellent results, the time complexity and resource usage are quite high for such methods. Additionally, these methods fail to incorporate the actual writing process when assessing text and instead solely focus on the content. Therefore, we proposed a framework for modeling textual data using keystroke-based features. Such methods pay attention to how a document or response was written, rather than the final text that was produced. These features are vastly different from the kind of features extracted from raw text but reveal information that is otherwise hidden. We hypothesized that pairing efficient machine learning techniques with keystroke log information should produce results comparable to transformer techniques, models which pay more or less attention to the different components of a text sequence in a far quicker time. Transformer-based methods dominate the field of NLP currently due to the strong understanding they display of natural language. We showed that models trained on keystroke log data are capable of effectively evaluating the quality of writing and do it in a significantly shorter amount of time compared to traditional methods. This is significant as it provides a necessary fast and cheap alternative to increasingly larger and slower LLMs.
Read More...Modular mimics of neuroactive alkaloids - design, synthesis, and cholinesterase inhibitory activity of rivastigmine analogs
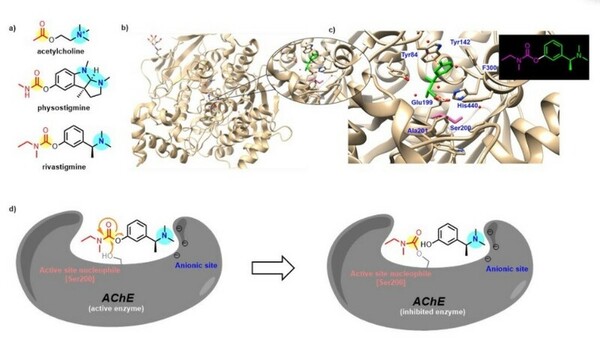
Naturally occurring neuroactive alkaloids are often studied for their potential to treat Neurological diseases. This team of students study Rivastigmine, a potent cholinesterase inhibitor that is a synthetic analog of physostigmine, which comes from the Calabar bean plant Physostigma venenosum. By comparing the effects of optimized synthetic analogs to the naturally occurring alkaloid, they determine the most favorable analog for inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), the enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to terminate neuronal transmission and signaling between synapses.
Read More...Using NLP to ascertain changes in the fast-fashion industry based on UN sustainable development goals
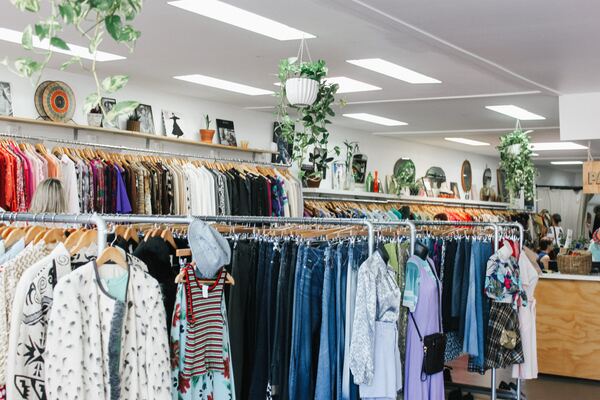

Here, the authors sought to evaluate the efforts of fast fashion clothing companies towards sustainability, specifically in regards to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. The authors used natural language processing to investigate the sustainability reports of fast fashion companies focusing on terms established by the UN. They found that the most consistently addressed areas were related to sustainable consumption/production, with a focus on health and well-being emerging during the recent pandemic.
Read More...