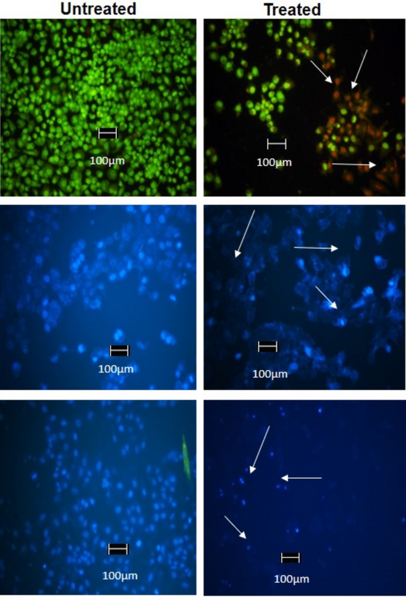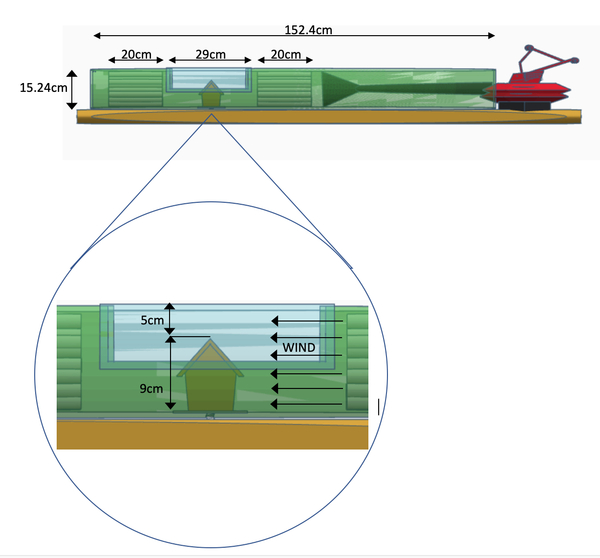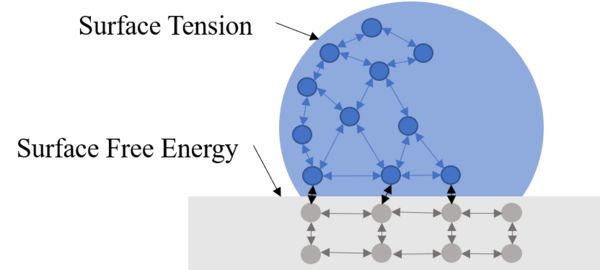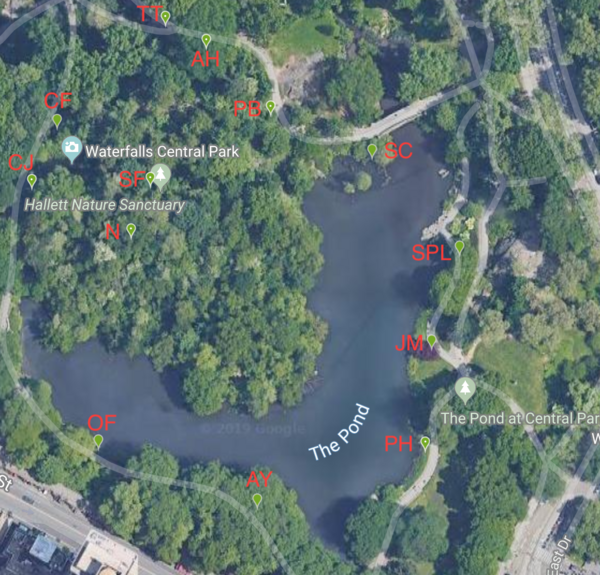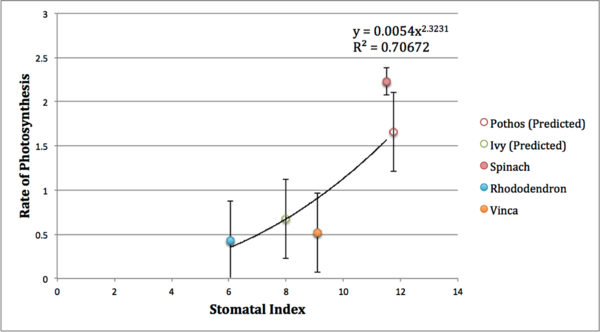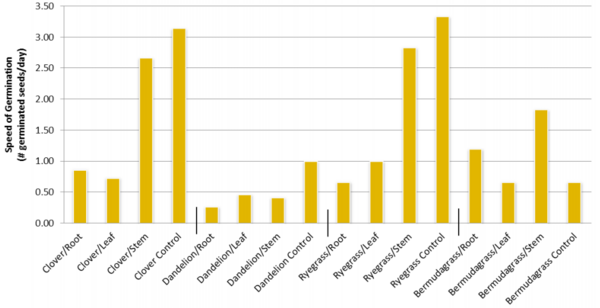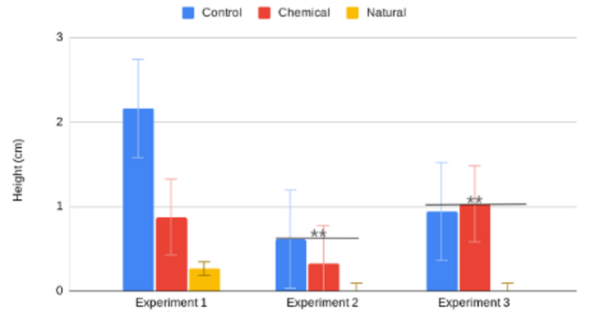
Agricultural fertilizer application is a key innovation in providing enough food to feed the world. Fertilizers come in various types and farmers must choose which fertilizer is the best for their applications. To learn more about the effectiveness of various fertilizers, Wilson and Rasmus studied the effects of natural and chemical fertilizers on growth of basil plants.
Read More...