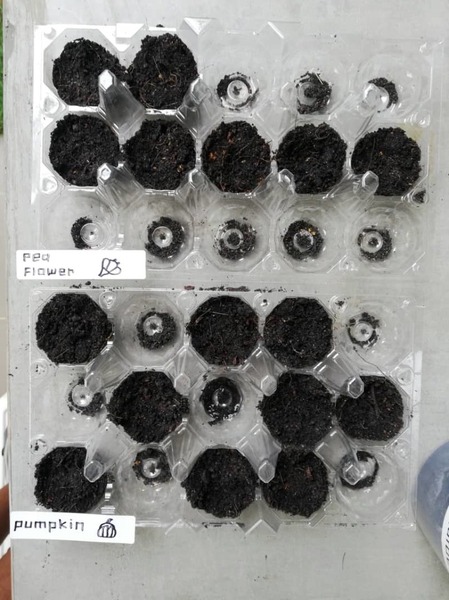

In this study, the authors investigate whether the addition of microbes from native soil enhanced the seed germination and growth of mung beans, pumpkins, and pea flower plants.
Read More...Microbes Cultured from Garden Soil Positively Impact Seed Germination and Plant Growth

In this study, the authors investigate whether the addition of microbes from native soil enhanced the seed germination and growth of mung beans, pumpkins, and pea flower plants.
Read More...The effect of floating plant on water purification: Comparison of the water purification capability of Water Hyacinth, Duckweed, and Azolla

Clean water is a necessity for every household, yet water pollution is a serious problem in many parts of the world and plays a major role in compromising water security in the 21st century. In this paper, the authors address the utility of several plants as natural water purifiers. They estimate the effectiveness of duckweed, hyacinth, and azolla in improving the quality of water from the Mithi river in India by measuring several metrics. They conclude that all three plants are effective in improving water quality, suggesting that these plants as eco-friendly options for water treatment.
Read More...Investigating the impact of short-chain fatty acids on myofiber dynamics and insulin sensitivity

The authors looked at the impacts of short-chain fatty acids on muscle fiber formation as well as insulin sensitivity using a model of mouse myoblasts.
Read More...Investigating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the cognitive dissonance of adolescents
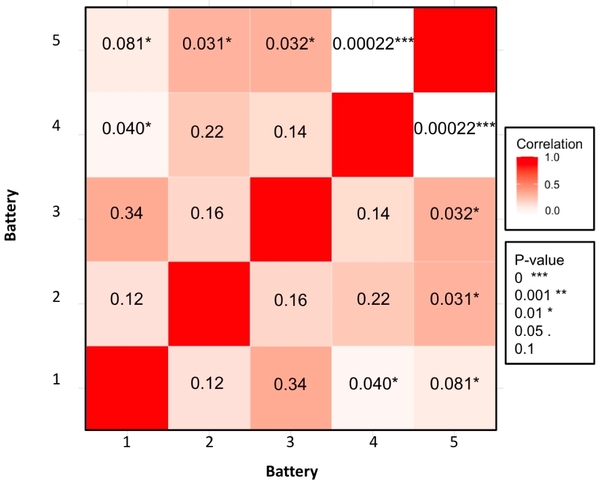
The authors survey adolescents about aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic to explore perspectives that may give rise to cognitive dissonance.
Read More...Environmentally-friendly graphene conductive ink using graphene powder, polystyrene, and waste oil
In this article, the authors propose an effective, environmentally-friendly method of producing conductive ink using expired waste oil, polystyrene, and graphene.
Read More...The effects of stress on the bacterial community associated with the sea anemone Diadumene lineata

In healthy ecosystems, organisms interact in a relationship that helps maintain one another's existence. Stress can disrupt this interaction, compromising the survival of some of the members of such relationships. Here, the authors investigate the effect of stress on the interaction between anemones and their microbiome. Their study suggests that stress changes the composition of the surface microbiome of the anemone D. lineata, which is accompanied by an increase in mucus secretion. Future research into the composition of this stress-induced mucus might reveal useful antimicrobial properties.
Read More...Elucidating the Genotoxicity of Synthetic Food Preservatives with the SOS Chromotest
.jpg)
Evidence suggests certain food preservatives may be genotoxic due to their ability to impair normal cellular pathways. The authors investigated the genotoxic potential and effects of commonly used synthetic food preservatives, specifically sodium nitrite, potassium sulfate, and hydrogen peroxide.
Read More...Enhanced soil fertility through seaweed-derived biochar: A comparative analysis with commercial fertilizers
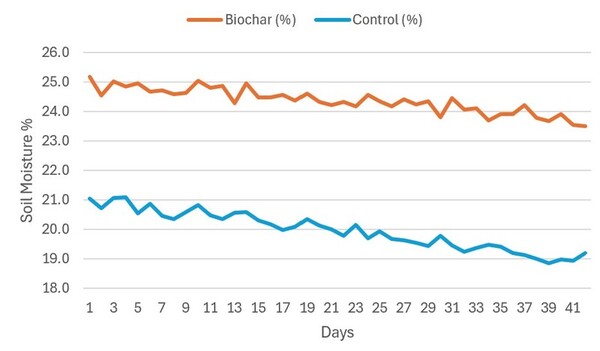
The study explored converting Gracilaria seaweed waste—known for releasing toxic hydrogen sulfide when decomposed—into biochar as a sustainable solution for waste management and soil improvement.
Read More...Effects of data amount and variation in deep learning-based tuberculosis diagnosis in chest X-ray scans
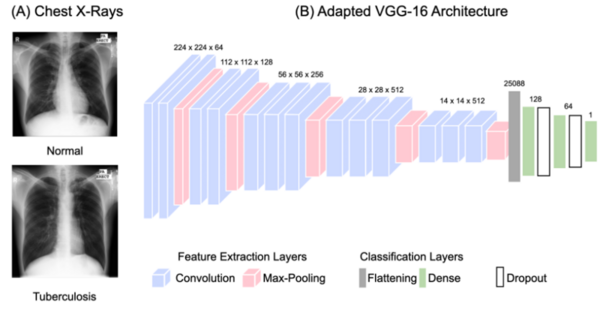
The authors developed and tested machine learning methods to diagnose tuberculosis from pulmonary X-ray scans.
Read More...Development of novel biodegradable bioplastics for packaging film using mango peels

Here the authors explored the development of biodegradable bioplastic films derived from mango peels as a sustainable solution to plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from fruit waste. They optimized the film's mechanical properties and water resistance through adjusting processing conditions and incorporating plasticizers and a hydrophobic coating, ultimately demonstrating its potential as a bacteriostatic and biodegradable alternative to conventional plastic food wrap.
Read More...