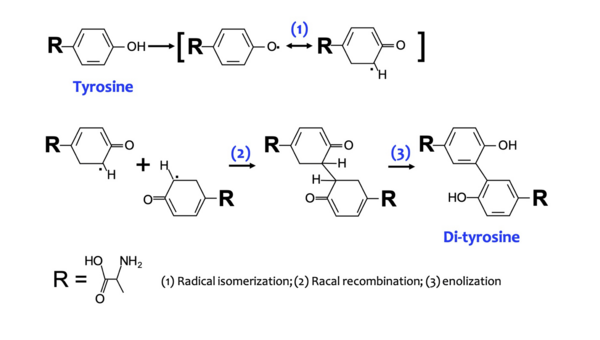
In this study, the authors develop a new hydrogel using photochemical crosslinking with bovine serum albumin and methylene blue. They find that this new hydrogel has some useful applications!
Read More...One-step photochemical crosslinking of native proteins is feasible in tyrosine-rich bovine serum albumin

In this study, the authors develop a new hydrogel using photochemical crosslinking with bovine serum albumin and methylene blue. They find that this new hydrogel has some useful applications!
Read More...Converting SiO2 wafers to hydrophobic using chlorotrimethylsilane
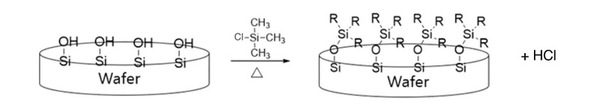
Semiconductors are the center of the fourth industrial revolution as they are key components for all electronics. Exposed wafers made of silicon (Si), which can easily oxidize, convert to silicon dioxide (SiO2). The surface of SiO2 wafers consists of many Si-OH bonds, allowing them to easily bond with water, resulting in a “wet” or hydrophilic condition. We sought to determine a way to modify the surface of SiO2 wafers to become hydrophobic to ensure safe wet cleaning.
Read More...Use of drone with sodium hydroxide carriers to absorb carbon dioxide from ambient air
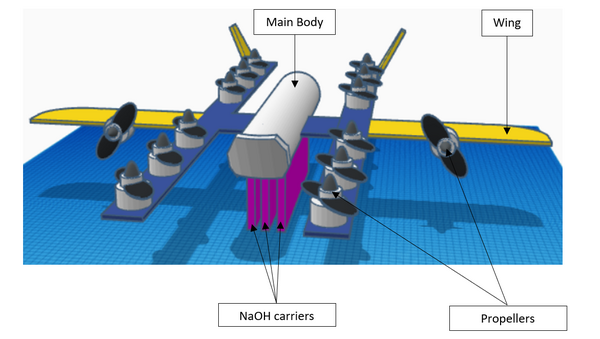
In this study, the authors address the current climate concern of high CO2 levels by testing solid forms of hydroxide for CO2 reduction and designing a drone to fly it in ambient air!
Read More...Combined Progestin-Estrogenic Contraceptive Pills May Promote Growth in Crop-Plants
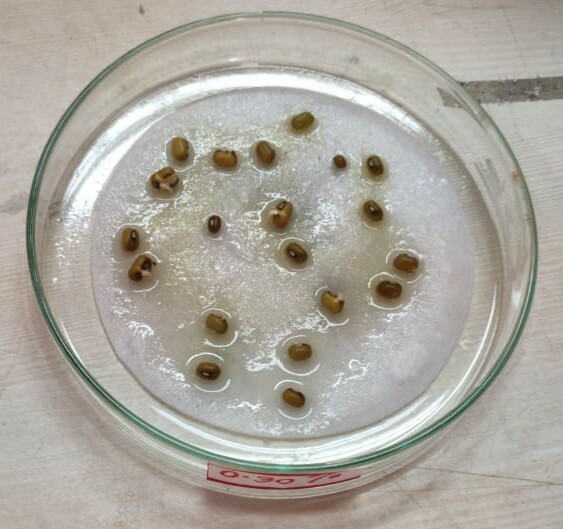

Ethinyl estradiol and progestin norgestrel are commonly present in contraceptive tablets and it is unknown how they affect the environment. In this study, the authors investigate the role that ethinyl estradiol and progestin norgestrel have on the growth of flowering plants. The percentage germination, embryonic and adventitious tissue proliferation, root length, and shoot length were measured in V. radiata and T. aestivum treated with each compound and results demonstrate that ethinyl estradiol and progestin norgestrel can induce growth in both plants at certain concentrations. These findings have important implications as societal use of chemicals increases and more make their way into the environment.
Read More...Use of yogurt bacteria as a model surrogate to compare household cleaning solutions
While resources on the safety of household cleaning products are plentiful, measures of efficacy of these cleaning chemicals against bacteria and viruses remain without standardization in the consumer market. The COVID pandemic has exasperated this knowledge gap, stoking the growth of misinformation and misuse surrounding household cleaning chemicals. Arriving at a time dire for sanitization standardization, the authors of this paper have created a quantifying framework for consumers by comparing a wide range of household cleaning products in their efficacy against bacteria generated by a safe and easily replicable yogurt model.
Read More...Novel environmentally friendly approach to wastewater treatment eliminates aluminum sulfate and chlorination
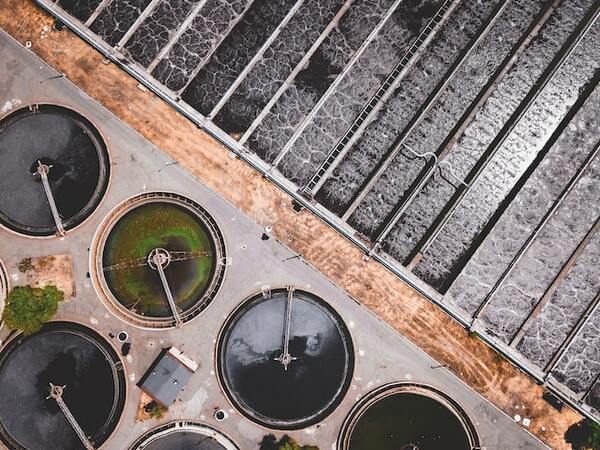

The authors tested environmentally-friendly alternatives to wastewater treatment chemicals, including activated charcoal for filtration and citrus peels for preventing bacterial growth.
Read More...Integrated Ocean Cleanup System for Sustainable and Healthy Aquatic Ecosystems
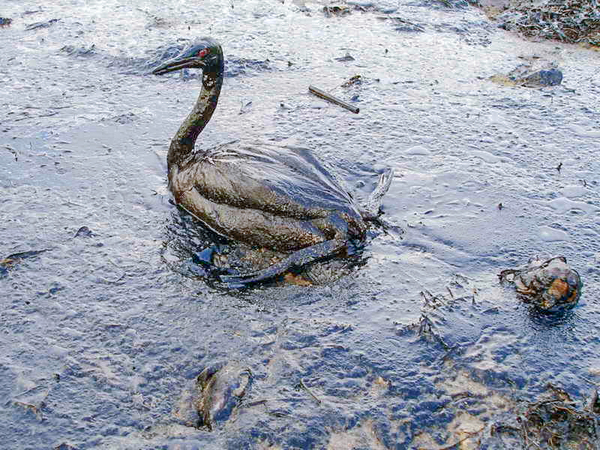

Oil spills are one of the most devastating events for marine life. Finding ways to clean up oil spills without the need for harsh chemicals could help decrease the negative impact of such spills. Here the authors demonstrate that using a combination of several biodegradable substances can effectively adsorb oil in seawater in a laboratory setting. They suggest further exploring the potential of such a combination as a possible alternative to commonly-used non-biodegradable substances in oil spill management.
Read More...Antimicrobial properties of common household spices on microbes cultured from two kitchen locations
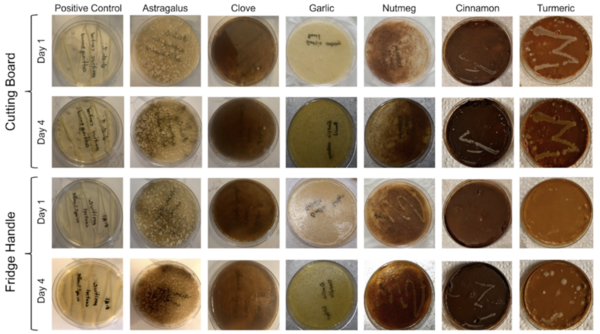
The number of bacterial infections in humans is rising, and a major contributor is foodborne illnesses, which affect a large portion of the population and result in many hospitalizations and deaths. Common household cleaners are an effective strategy to combat foodborne illness, but they are often costly and contain harmful chemicals. Thus, the authors sought to test the antimicrobial effectiveness of spices (clove, nutmeg, astragalus, cinnamon, turmeric, and garlic) on microbes cultured from refrigerator handles and cutting boards. Results from this study demonstrate long-lasting, antimicrobial effects of multiple spices that support their use as alternatives to common household cleaners.
Read More...Decolorization of textile dyes by edible white rot fungi

As fast fashion explodes in popularity, the fashion industry remains one of the most prominent industries responsible for pollution. This pollution includes a lack of treatment for textile dyes that remain toxic or carcinogenic as they persist in wastewater. To resolve this, the authors of this study set out to determine the efficacy of using edible white rot fungi for cell-based biodegradation of textile dyes into harmless chemicals. This method takes advantage of fungi found in excess from the fungi industry, decreasing food waste while addressing textile waste in tandem.
Read More...The Effects of Micro-Algae Characteristics on the Bioremediation Rate of Deepwater Horizon Crude Oil
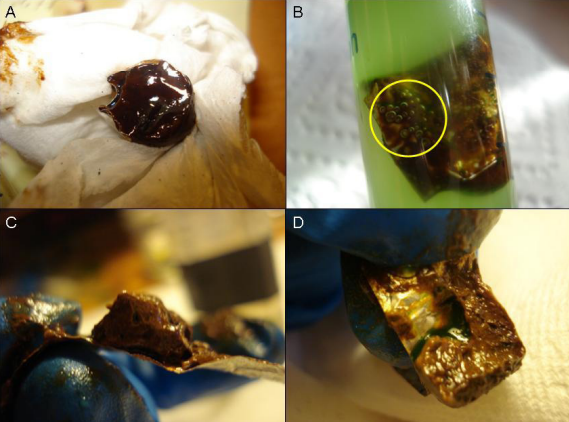
Environmental disasters such as the Deepwater Horizon oil spill can be devastating to ecosystems for long periods of time. Safer, cheaper, and more effective methods of oil clean-up are needed to clean up oil spills in the future. Here, the authors investigate the ability of natural ocean algae to process crude oil into less toxic chemicals. They identify Coccochloris elabens as a particularly promising algae for future bioremediation efforts.
Read More...