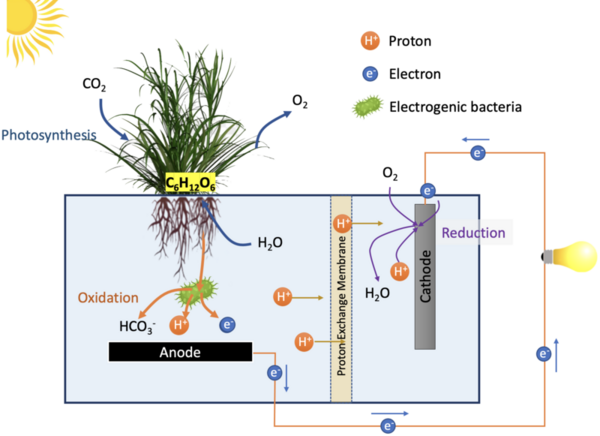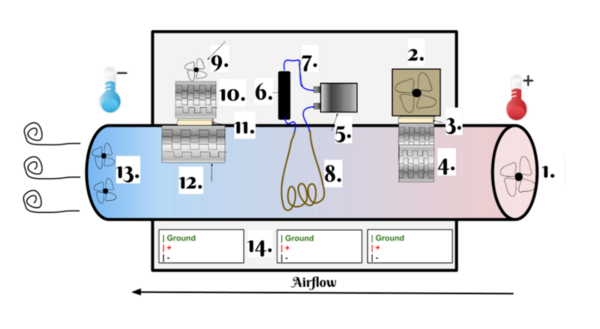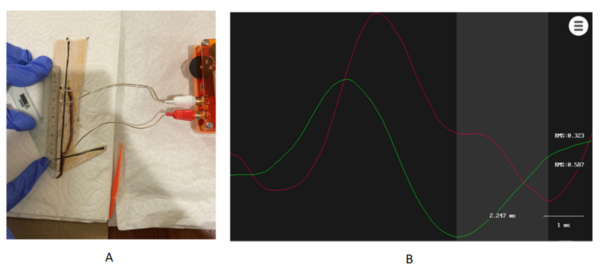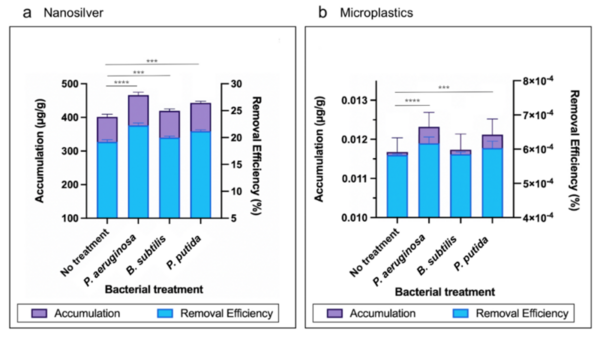
The authors looked at phytoremediation, the process by which plants are used to remove pollutants from our environment, and the ability of Lemna minor to perform phytoremediation in various simulated polluted environments. The authors found that L. minor could remove pollutants from the environment and that the addition of bacteria increased this removal.
Read More...
%20final%202-5-23.jpg)