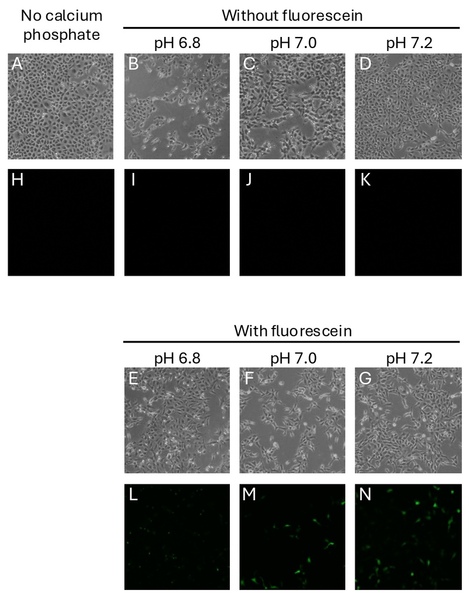
This study investigated the impact of pH on the efficiency of calcium phosphate, used as a drug delivery agent.
Read More...Higher pH level increases the efficacy of calcium phosphate-mediated intracellular delivery

This study investigated the impact of pH on the efficiency of calcium phosphate, used as a drug delivery agent.
Read More...Impact of aluminum surface area on the rate of reaction with aqueous copper (II) chloride solutions

In this article the authors looked at how temperature was impacted when alumnium was added in various forms to aqueous copper(II) solutions. Their study investigates the impact of surface area on chemical reactions.
Read More...Impact of Soil Productivity on the Growth of Two Meyer Lemon Trees

Here, the authors aimed to apply home soil testing to identify the cause of the growth differences between two lemon trees. They hypothesized that differences in physical and chemical soil characteristics were influencing differences in soil productivity and plant growth. Overall, the study demonstrated the effectiveness of home soil testing to characterize soils and help homeowners solve common gardening problems.
Read More...The impact of political ideologies on renewable energy adoption
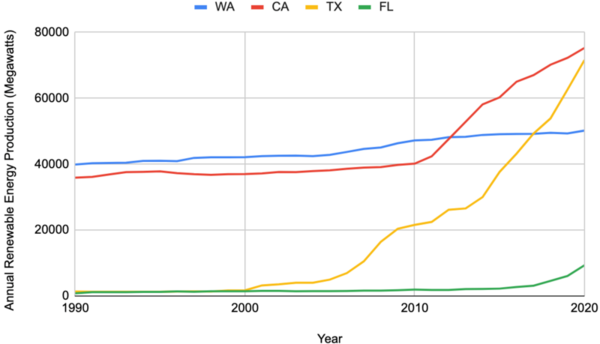
The authors compare rates of renewable energy adoption between states that historically vote for democrats versus republicans in presidential elections.
Read More...The impact of greenhouse gases, regions, and sectors on future temperature anomaly with the FaIR model
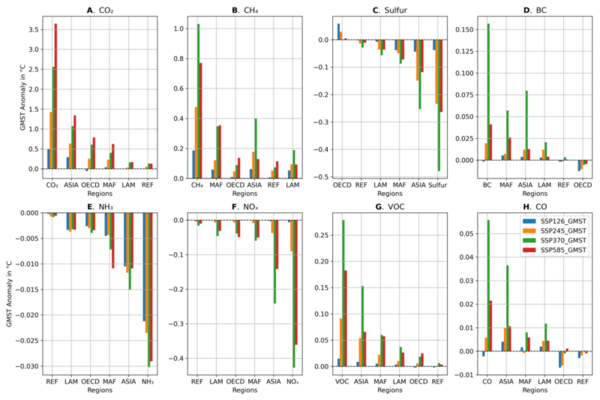
This study explores how different economic sectors, geographic regions, and greenhouse gas types might affect future global mean surface temperature (GMST) anomalies differently from historical patterns. Using the Finite Amplitude Impulse Response (FaIR) model and four Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) — SSP126, SSP245, SSP370, and SSP585 — the research reveals that future contributions to GMST anomalies.
Read More...Influence of socioeconomic status on academic performance in virtual classroom settings

In this study, the authors conduct a survey to evaluate the impact of household socioeconomic status on effectiveness of distance learning for students.
Read More...The impact of timing and magnitude of the El Niño- Southern Oscillation on local precipitation levels and temperatures in the Bay Area
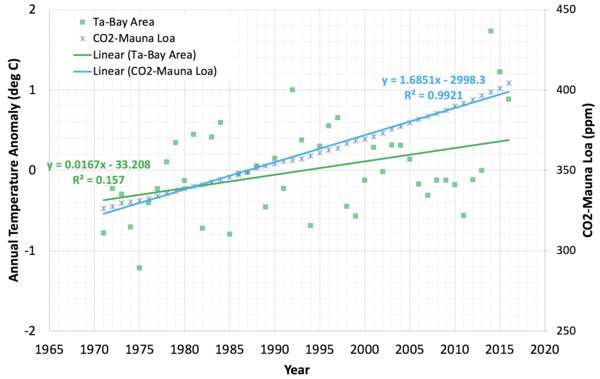
Understanding the relationships between temperature, MEI, SPI, and CO2 concentration is important as they measure the major influencers of California’s regional climate: temperature, ENSO, precipitation, and atmospheric CO2. In this article, the authors analyzed temperature, Multivariate El Niño-Southern Oscillation Index (MEI), and Standard Precipitation Index (SPI) data from the San Francisco Bay Area from 1971 to 2016. They also analyzed CO2 records from Mauna Loa, HI for the same time period, along with the annual temperature anomalies for the Bay Area.
Read More...Exploring the resonant vibration of a cello with the finite element method
Emotional and Psychological Effect of Music on People

Nolt and Elwonger examine how different types of music impact our emotional and physical states. They found that music can influence a subject's emotional state, with sad music inspiring sadness and exciting music bringing excitement. They were not able to find a clear relationship between heart rate and music type. Music's effect on emotional state can be useful when designing novel therapies for emotional and mental disorders.
Read More...Observing food and density effects on the reproductive strategies of Heterandria formosa
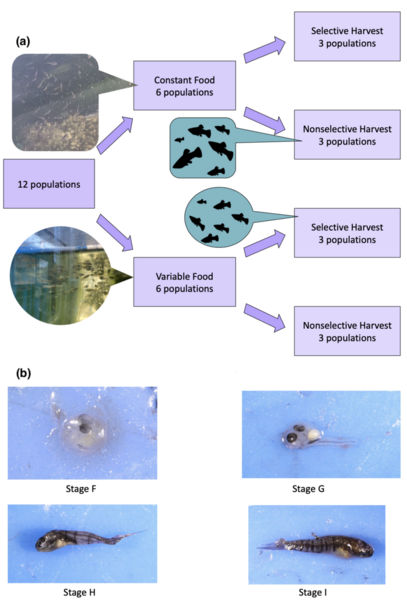
The authors looked at the impact of different harvest and feeding treatments on Heterandria formosa over three generations as a model for changes in marine ecosystems.
Read More...