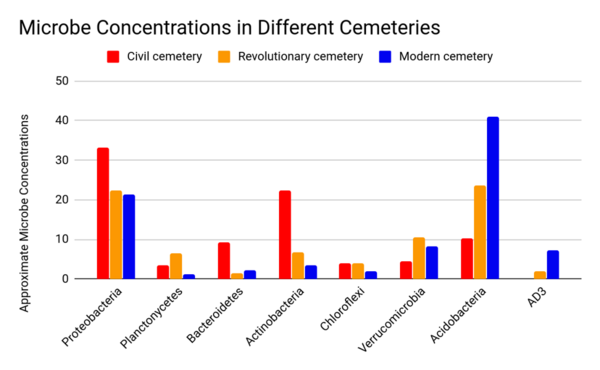
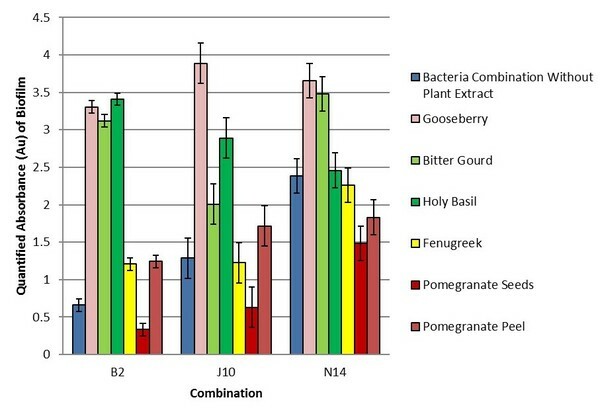
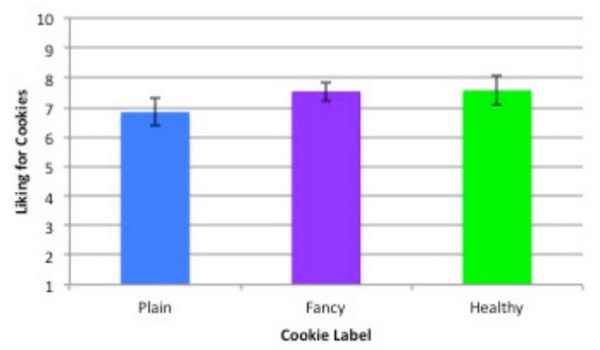
Bennett and Joykutty test whether growth hormone directly or indirectly affected the rate at which cartilage renewed itself. Growth hormone could exert a direct effect on cartilage or chondrocytes by modifying the expression of different genes, whereas an indirect effect would come from growth hormone stimulating insulin-like growth factor. The results from this research support the hypothesis that growth hormone increases proliferation rate using the direct pathway. This research can be used in the medical sciences for people who suffer from joint damage and other cartilage-related diseases, since the results demonstrated conditions that lead to increased proliferation of chondrocytes. These combined results could be applied in a clinical setting with the goal of allowing patient cartilage to renew itself at a faster pace, therefore keeping those patients out of pain from these chondrocyte-related diseases.
Read More...