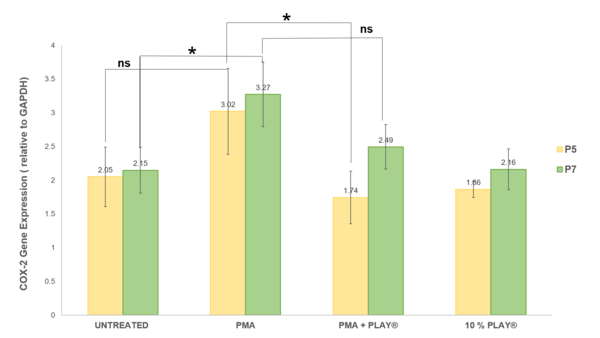
Here recognizing the importance of urban green space for the health of humans and other organisms, the authors investigated if mathematical modeling can be used to develop an urban greenery management plan with high eco-sustainability by calculating the composition of a plant community. They optimized and tested their model against green fields in a Beijing city park. Although the compositions predicted by their models differed somewhat from the composition of testing fields, they conclude that by using a mathematical model such as this urban green space can be finely designed to be ecologically and economically sustainable.
Read More...