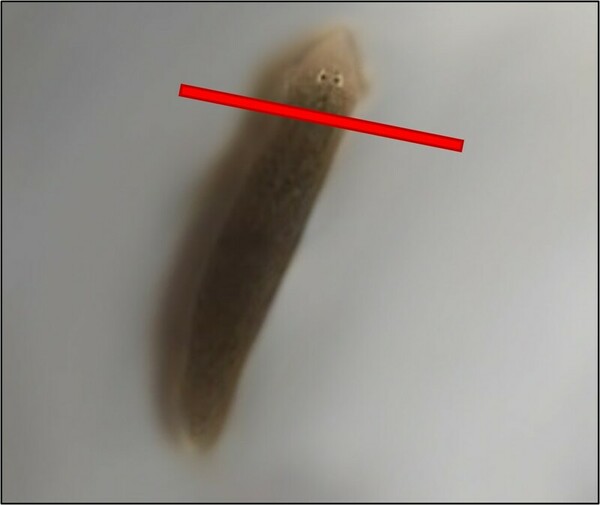
The consumption of sugar substitute non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS) has dramatically increased in recent years. Despite being advertised as a healthy alternative, NNS have been linked to adverse effects on the body, such as neurodegenerative diseases (NDs). In NDs, neural stem cell function is impaired, which inhibits neuron regeneration. The purpose of this study was to determine if the NNS acesulfame potassium (Ace-K) and neotame affect planaria neuron regeneration rates. Since human neurons may regenerate, planaria, organisms with extensive regenerative capabilities due to stem cells called neoblasts, were used as the model organism. The heads of planaria exposed to either a control or non-toxic concentrations of NNS were amputated. The posterior regions of the planaria were observed every 24 hours to see the following regeneration stages: (1) wound healing, (2) blastema development, (3) growth, and (4) differentiation. The authors hypothesized that exposure to the NNS would slow planaria regeneration rates. The time it took for the planaria in the Ace-K group and the neotame group to reach the second, third, and fourth regeneration stage was significantly greater than that of the control. The results of this study indicated that exposure to the NNS significantly slowed regeneration rates in planaria. This suggests that the NNS may adversely impact neoblast proliferation rates in planaria, implying that it could impair neural stem cell proliferation in humans, which plays a role in NDs. This study may provide insight into the connection between NNS, human neuron regeneration, and NDs.
Read More...

.png)
