Comparative life cycle analysis: Solvent recycling and improved dewatering scenarios in PHB plastic production
(1) Kang Chiao International School, (2) Graduate Institute of Environmental Engineering, National Taiwan University, (3) Taipei Fuhsing Private School
https://doi.org/10.59720/24-107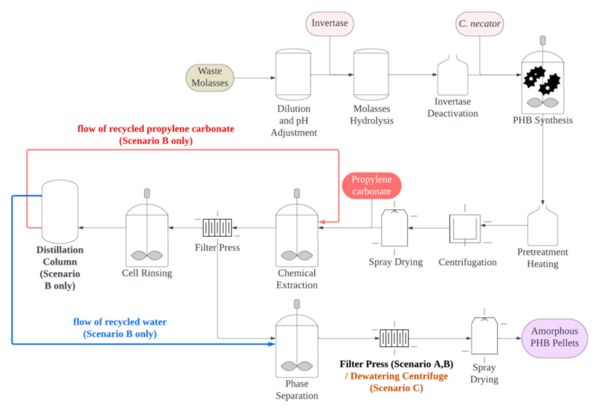
Bioplastics have become a major focus of international research aiming to achieve sustainability. With the high technical similarity between bioethanol and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) bioplastic production, there lies an opportunity for Taiwan’s bioethanol producers to expand into the growing bioplastics industry. Using SimaPro software and the ReCiPe 2016 Hierarchist assessment method to conduct life cycle analysis, this investigation aimed to provide insight into sustainable PHB production. Synthesizing data from literature, we determined the types and quantities of inputs and outputs in PHB production, then used SimaPro’s built-in Ecoinvent datasets to tally the environmental impact scores of raw materials and pollutants. We compared the environmental impact of a standard PHB plastic production process to two proposed scenarios: one incorporating solvent recycling through distillation and another using an optimized dewatering process that replaced filter presses with centrifuges. According to existing studies, we hypothesized both solvent recycling and dewatering centrifugation scenarios would have lower overall environmental impact than the standard production process. However, our results revealed that only the dewatering centrifugation scenario achieved an overall decrease in environmental impact across 17 ReCiPe impact categories, ranging from carbon emissions and ecotoxicity to land use and water consumption. On the other hand, incorporating solvent recycling led to a 70% decrease in mineral resource consumption and a 42% decrease in water consumption but also a 45% increase in carbon emissions. Due to their energy-intensive nature, current distillation technologies for solvent recycling cannot yet significantly decrease the impact of PHB production; instead, it is more effective for manufacturers to focus on optimized dewatering to reduce environmental impact.
This article has been tagged with: