Explainable AI tools provide meaningful insight into rationale for prediction in machine learning models
(1) Lebanon Trail High School, (2) Department of Computer Science, University of Texas
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-341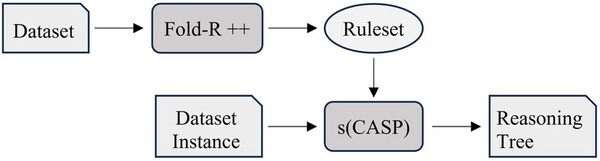
The advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms in artificial intelligence (AI) are complex, with limited insight into the interpretability of these models. Explainable AI (XAI) is an emerging research field that seeks to clarify the rationale behind the outcomes predicted by ML and AI models. We hypothesized that contemporary XAI tools, such as the FOLD-R++ (Improved First Order Learner of Default with Recursive Rules) algorithm and the s(CASP) (System for Answer Set Programming with Constraints) utility, could achieve accuracy within 5% of those from well-known ML algorithms. FOLD-R++ offers meaningful reasoning through justification trees for predicted outcomes, similar to LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations) used with ML algorithms. We employed FOLD-R++, an automated inductive learning algorithm, and s(CASP), a reasoning interpreter utility, on ten binary classification datasets from various domains. FOLD-R++ consistently produced accuracy within 5% of those from ML algorithms across all datasets and did so in less processing time in most of the tests. The rulesets generated by FOLD-R++ were processed in s(CASP), which uses constraints in Answer Set Programming to create easily understandable reasoning trees. Finally, ML models were run through LIME to generate graphical representations highlighting dominant parameters affecting outcomes. This analysis approach can be a standard pattern for gaining insights into binary classification machine learning problems.
This article has been tagged with: