Investigating the role of anti-CRISPR proteins in horizontal gene transfer aboard the ISS
Geethika Burugupally (1), Seunga Choo (2), Taylor Lanosky (3)
(1) Lake Washington High School, (2) Fred Hutch Cancer Center, (3) Harvard University
Abstract
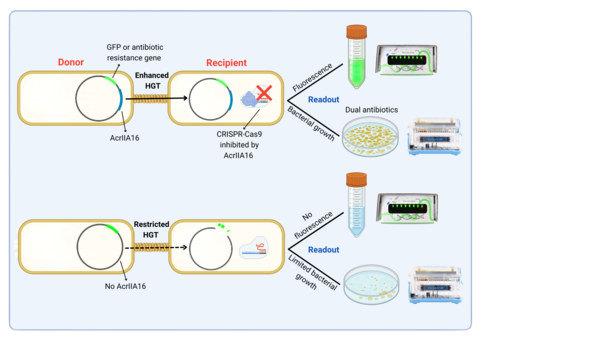
Microbes in spacecrafts are exposed to stressors, including microgravity and radiation, which can drive adaptive mechanisms like horizontal gene transfer (HGT). HGT can spread antibiotic resistance, strengthen biofilms, and destabilize probiotics, posing risks to astronaut health. On Earth, naturally occurring microbial CRISPR-Cas systems restrict HGT by blocking foreign DNA acquisition, but naturally expressed Anti-CRISPR (Acr) proteins inhibit CRISPR-Cas systems, promoting HGT. While Acr proteins effectively inhibit CRISPR-Cas systems on Earth, it is unknown how spaceflight stressors affect their expression, activity, and impact on HGT. We hypothesize that since HGT enhances microbial survival in space, space stressors will increase Acr protein expression or activity to enhance CRISPR-Cas9 inhibition and HGT. To test this, we will engineer E. coli Nissle strains as HGT donors and recipients: the donor will carry a plasmid encoding SpyCas9 and T7 polymerase, while the recipient will carry a plasmid with GFP under a T7 promoter and AcrIIA16 —an Acr protein that inhibits multiple Cas9 variants, including SpyCas9— under native promoters of varying strength. Since the donor lacks T7 polymerase, GFP expression will occur only if T7 polymerase from the recipient initiates transcription from the donor’s T7 promoter, signaling HGT. A parallel conjugation assay will confirm HGT via antibiotic resistance: the donor will carry kanamycin resistance, the recipient chloramphenicol resistance, and only transconjugants will grow on dual-antibiotic plates. miniPCR™ will verify transconjugants by amplifying the kanamycin resistance gene, ruling out spontaneous mutation. In both assays, AcrIIA16 expression will be tracked through GFP fusion. If AcrIIA16 inhibits CRISPR-Cas9, promoting HGT, it will be detected in both assays. Parallel experiments on Earth and in space will compare HGT rates and AcrIIA16 function. Results will illuminate how Acr proteins regulate HGT in space, informing strategies to limit antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation or harness Acr proteins for CRISPR-Cas9 regulation in spaceflight.