Novel anticancer effects of melatonin and berberine via signaling pathways in colorectal cancer and lymphoma
(1) TVT Community Day School, (2) Chint Power Systems America, (3) SCI Research Institute
https://doi.org/10.59720/24-201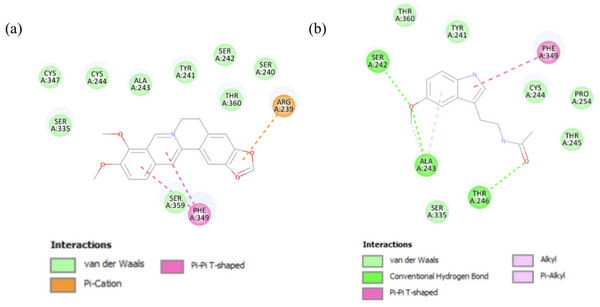
Colorectal cancer (CRC) and lymphoma are leading causes of death worldwide. Berberine, a component of the Chinese herb Coptis chinensis, and melatonin, produced endogenously by humans and obtained in the diet, have similar anticancer effects of inducing apoptosis and modifying signaling pathways involved in cancer. Current cancer treatments like radiotherapy are toxic, costly, and have a limited number of targets. We hypothesized that berberine and melatonin would have synergistic anticancer effects on CRC and lymphoma cancer cells through inducing apoptosis and mitigating metastasis. Different dilutions of melatonin and berberine were used to treat cancerous COLO320 (CRC) and U937 (lymphoma) cells, with healthy CCD18 colon cells as a control. Molecular docking was conducted between melatonin and berberine with genes in major cancer pathways. There was a significant, dose-dependent decrease in cancer cell proliferation after 24-hour and 96-hour berberine-melatonin combined treatment. There was a significant decrease in cell adhesion. Also, there was a significant increase in the activity of caspase by a factor of 5x, which led to the induction of apoptosis in cancer cells. Furthermore, berberine and melatonin caused a significant downregulation of BDNF and MMP9 expression. In the molecular docking results, berberine and melatonin bound very strongly to MMP9 at the same location, correlating with the ELISA assay results and suggesting their synergistic properties. In conclusion, the hypothesis that berberine and melatonin have potential synergistic anticancer effects compared to berberine and melatonin alone is supported. In the future, melatonin and berberine could be used to strengthen or as an alternative to conventional cancer treatments.
This article has been tagged with: