How artificial intelligence deep learning models can be used to accurately determine lung cancers
(1) The Hockaday School, (2) University of Oxford
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-232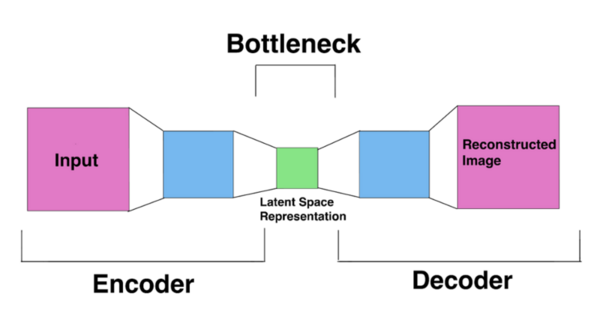
Disease is a highly stressed topic in current society, especially the importance of early diagnosis and disease prevention with the help of new technology. Doctors can diagnose diseases like lung cancers, but the process can be more time-consuming, expensive, and inaccurate compared to relying on technology alone. Although previous applications of artificial intelligence exist in the clinical world, our goal was to find which deep learning model would be most accurate in predicting lung cancer. We hypothesized that autoencoders would perform better than other deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks (CNN) and pre-trained models based on the strength and reliability of the data created by the encoder for classification. We studied Kaggle dataset “Chest CT-Scan Images Dataset,” which contains images of both benign and malignant tumors, with malignant categories of lung squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. We trained and tested each model with this dataset on the machine learning tool Google Colaboratory. Based on the results, the pre-trained CNN model had the accuracy at correctly detecting lung cancers, while the autoencoder had the lowest compared to the others. Overall, our results do not support our original hypothesis and instead show that pre-trained models may be more applicable in lung cancer diagnosis.
This article has been tagged with: