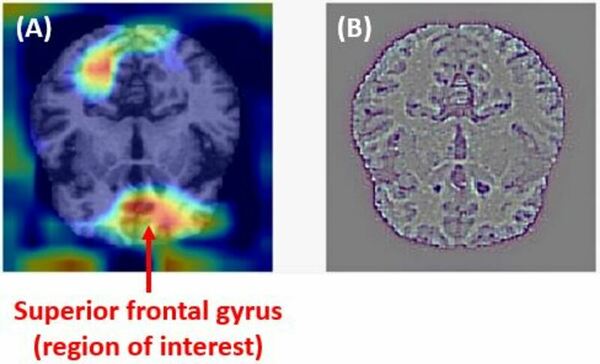
In the battle against Alzheimer's disease, early detection is critical to mitigating symptoms in patients. Here, the authors use a collection of MRI scans, layering with deep learning computer modeling, to investigate early stages of AD which can be hard to catch by human eye. Their model is successful, able to outperform previous models, and detected regions of interest in the brain for further consideration.
Read More...