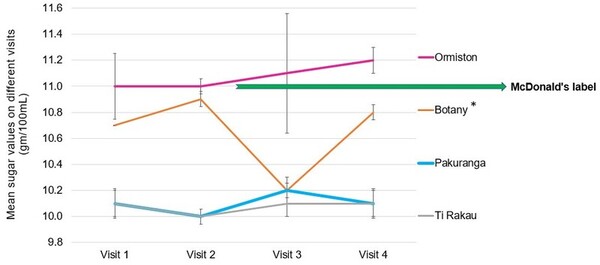
The authors looked at public knowledge regarding suggested daily limits for sugar intake and then looked at how sugar levels vary in the same drink obtained from different sources and across different days.
Read More...Knowledge gaps for recommended daily sugar intake and variations in McDonald’s Coca-Cola sugar levels

The authors looked at public knowledge regarding suggested daily limits for sugar intake and then looked at how sugar levels vary in the same drink obtained from different sources and across different days.
Read More...Lung cancer AI-based diagnosis through multi-modal integration of clinical and imaging data
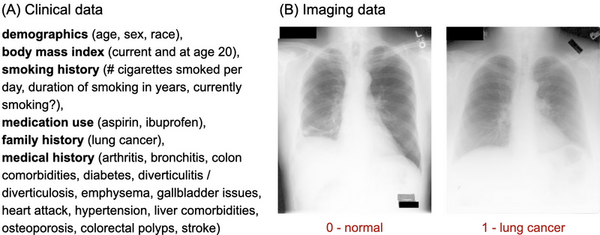
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...Investigating the anticancer effects of Uvularia perfoliata
This paper investigates the potential anticancer properties of Uvularia perfoliata by testing its effects on the viability of uveal melanoma cells.
Read More...Risk-adjusted return measures for selecting optimal mutual fund investment portfolios

The authors looked at different combinations of risk-adjusted return measures to determine which combination would provide an optimal return for investors. They found that different combinations performed better dependent on investment timeframe.
Read More...Validating DTAPs with large language models: A novel approach to drug repurposing

Here, the authors investigated the integration of large language models (LLMs) with drug target affinity predictors (DTAPs) to improve drug repurposing, demonstrating a significant increase in prediction accuracy, particularly with GPT-4, for psychotropic drugs and the sigma-1 receptor. This novel approach offers to potentially accelerate and reduce the cost of drug discovery by efficiently identifying new therapeutic uses for existing drugs.
Read More...The characterizations and the anonymity of comments: A case study on Lizzo’s videos
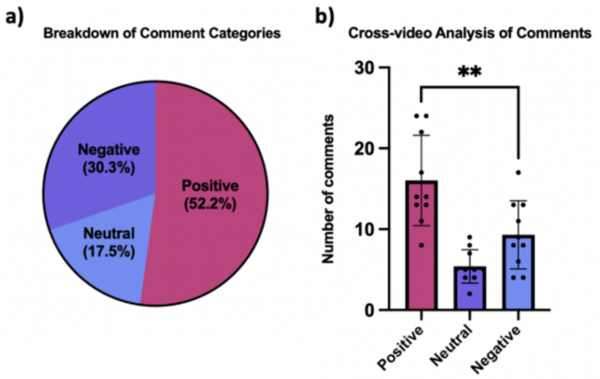
Social media, especially among adolescents, has become a popular communication tool, but its link to negative mental health outcomes is a growing concern. This study analyzed public comments on Lizzo's social media, focusing on the nature of praise and criticism.
Read More...The correlation between bacteria and colorectal cancer
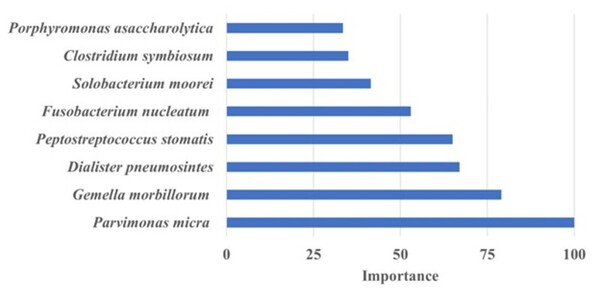
The authors looked at abundance of bacteria in stool samples from patients with colorectal cancer compared to controls. They found different bacteria that was more prevalent in patients with colorectal cancer as well as bacteria in control patients that may indicate a beneficial gut microbiome.
Read More...Convolutional neural network-based analysis of pediatric chest X-ray images for pneumonia detection
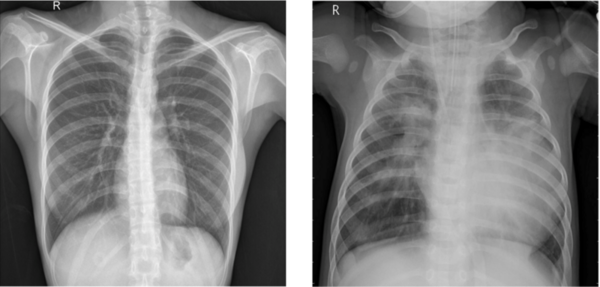
The authors test various machine learning models to improve the accuracy and efficiency of pneumonia diagnosis from X-ray images.
Read More...Digestion products of bread and cheese cause addictive behavior in a planaria model
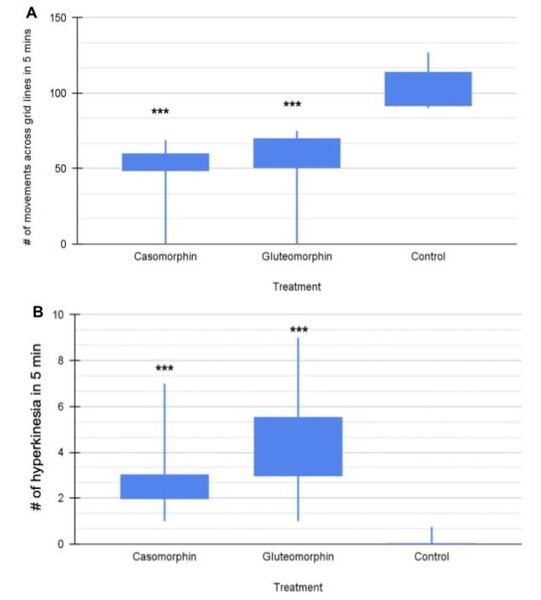
The authors looked at two peptides, gluteomorphin and casomorphin, that are present after the digestion of bread and cheese. As these peptides can bind opioid receptors the authors want to know if they could be addictive in the same way as conventional opioids (i.e., morphine) are known to be. Their results in a planaria model suggest that both of these peptides are addictive.
Read More...Stress and depression among individuals with low socioeconomic status during economic inflation
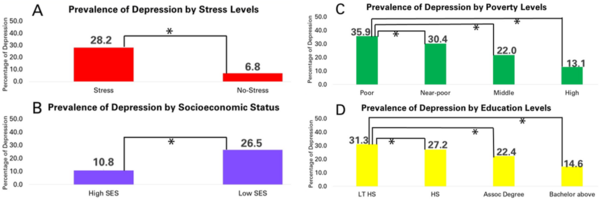
The authors use the Census Household Pulse Survey issued by the US Census Bureau to examine the prevalence of stress and depression among people across socioeconomic statuses.
Read More...