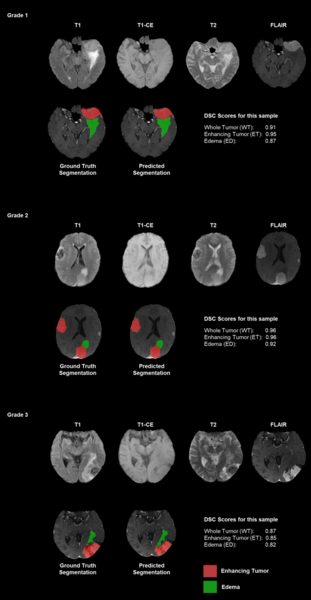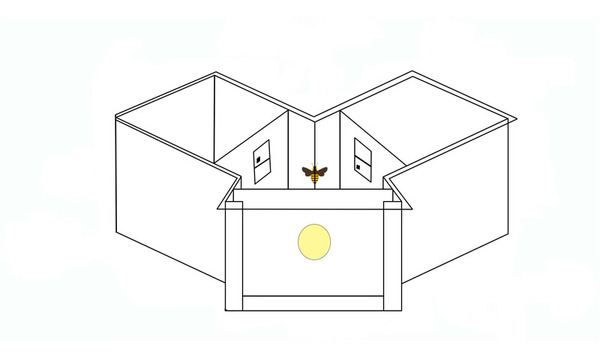
Modern artificial neural networks have been remarkably successful in various applications, from speech recognition to computer vision. However, it remains less clear whether they can implement abstract concepts, which are essential to generalization and understanding. To address this problem, the authors investigated the above vs. below task, a simple concept-based task that honeybees can solve, using a conventional neural network. They found that networks achieved 100% test accuracy when a visual target was presented below a black bar, however only 50% test accuracy when a visual target was presented below a reference shape.
Read More...