The authors looked at the correlation between C reactive protein levels and neurological deficits in patients who had suffered an ischemic stroke.
Read More...C reactive protein and risk of neurological deficits and disability in patients with acute ischemic stroke

The authors looked at the correlation between C reactive protein levels and neurological deficits in patients who had suffered an ischemic stroke.
Read More...Association of depression and suicidal ideation among adults with the use of H2 antagonists
In this study, the authors investigate associations between use of histamine H2 receptor antagonists and suicidal ideation in different age groups.
Read More...Correlating inlet gas composition to conversion efficiency in plasma-assisted landfill gas reforming
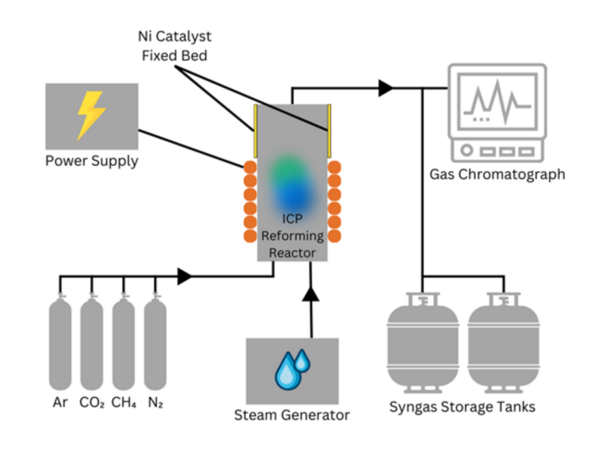
The escalating crisis of climate change, driven by the accumulation of greenhouse gases from human activities, demands urgent and innovative solutions to curb rising global temperatures. Plasma-based methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) reforming offers a promising pathway for carbon capture and the sustainable production of hydrogen fuel and syngas components. To advance this technology, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and selectivity, it is essential to enhance the conversion efficiencies of CO2 and CH4.
Read More...Predicting baseball pitcher efficacy using physical pitch characteristics

Here, the authors sought to develop a new metric to evaluate the efficacy of baseball pitchers using machine learning models. They found that the frequency of balls, was the most predictive feature for their walks/hits allowed per inning (WHIP) metric. While their machine learning models did not identify a defining trait, such as high velocity, spin rate, or types of pitches, they found that consistently pitching within the strike zone resulted in significantly lower WHIPs.
Read More...Predicting and explaining illicit financial flows in developing countries: A machine learning approach
The authors looked at the ability of different machine learning algorithms to predict the level of financial corruption in different countries.
Read More...Epileptic seizure detection using machine learning on electroencephalogram data
The authors use machine learning and electroencephalogram data to propose a method for improving epilepsy diagnosis.
Read More...Exponential regression analysis of the Canadian Zero Emission Vehicle market’s effects on climate emissions in 2030

Here, the authors explored how the sale and use of electric vehicles could reduce emissions from the transport industry in Canada. By fitting the sale of total of electric vehicles with an exponential model, the authors predicted the number of electric vehicle sales through 2030 and related that to the average emission for such vehicles. Ultimately, they found that the sale and use of electric vehicles alone would likely not meet the 45% reduction in emissions from the transport industry suggested by the Canadian government
Read More...Comparative study of machine learning models for water potability prediction
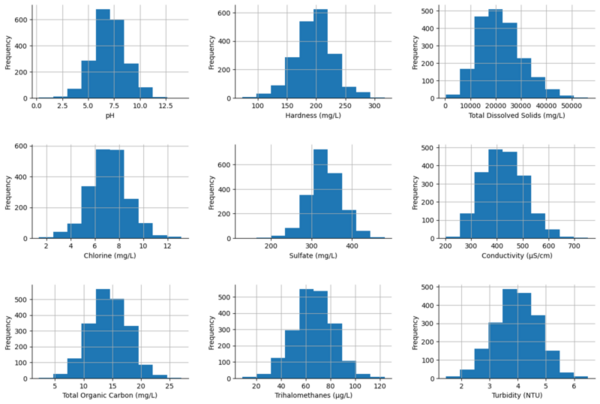
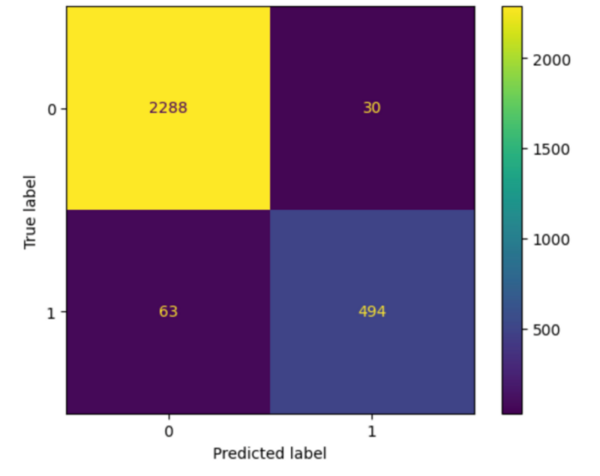
The global issue of water quality has led to the use of machine learning models, like ANN and SVM, to predict water potability. However, these models can be complex and resource-intensive. This research aimed to find a simpler, more efficient model for water quality prediction.
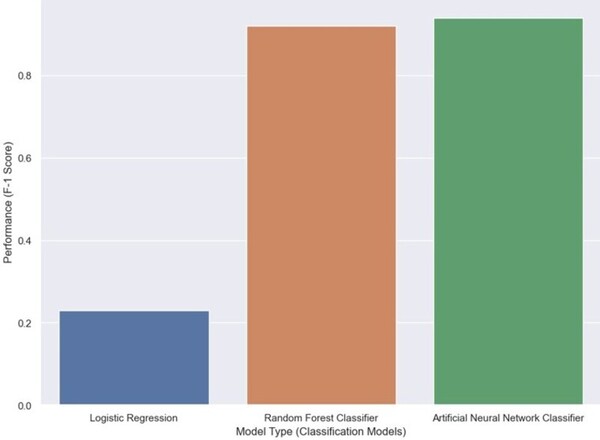
Read More...Machine Learning Algorithm Using Logistic Regression and an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for Early Stage Detection of Parkinson’s Disease
Despite the prevalence of PD, diagnosing PD is expensive, requires specialized testing, and is often inaccurate. Moreover, diagnosis is often made late in the disease course when treatments are less effective. Using existing voice data from patients with PD and healthy controls, the authors created and trained two different algorithms: one using logistic regression and another employing an artificial neural network (ANN).
Read More...Predicting clogs in water pipelines using sound sensors and machine learning linear regression
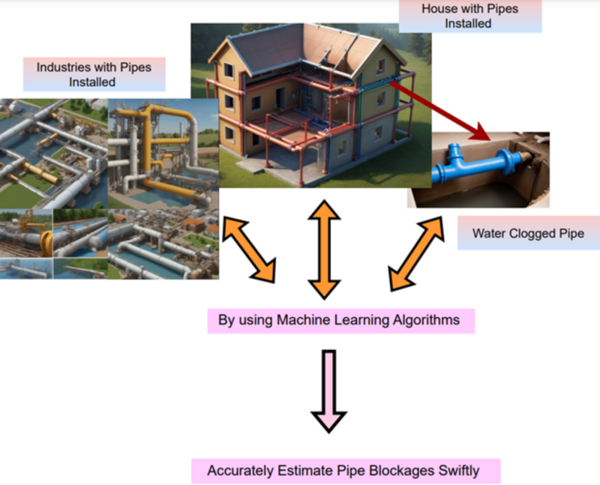
The authors looked the ability of sound sensors to predict clogged pipes when the sound intensity data is run through a machine learning algorithm.
Read More...