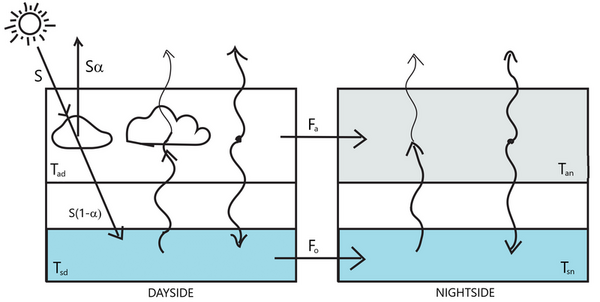
The authors assessed the atmospheric and oceanic parameters necessary for tidally-locked exoplanets to be habitable.
Read More...Ocean, atmosphere, and cloud quantity on the surface conditions of tidally-locked habitable zone planets

The authors assessed the atmospheric and oceanic parameters necessary for tidally-locked exoplanets to be habitable.
Read More...Testing filtration capabilities of household fabrics for protection against airborne contaminants
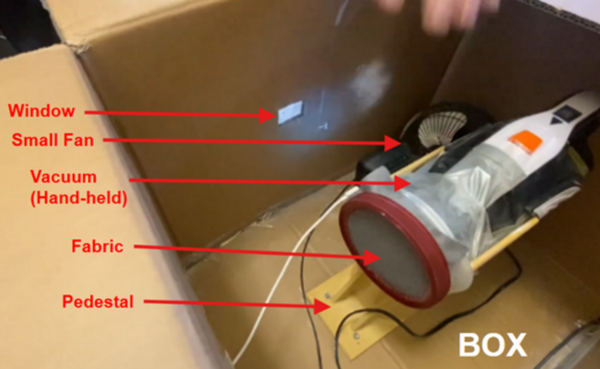
Toxic particulates in the atmosphere pose significant health risks, and while modern masks can help reduce inhalation of these pollutants, their availability may be limited during health crises. This study evaluated the effectiveness of household fabrics (cotton, fleece, wool, and rayon) as particulate filters, finding that cotton outperformed the others in filtration efficiency, while rayon was the least effective. The findings suggest that cotton is a preferable alternative for filtration purposes, while rayon should be avoided.
Read More...Impact of Silverado Fire on soil carbon

Soil stores three times more carbon than the atmosphere, making small changes in its storage and release crucial for carbon cycling and climate models. This study examined the impact of the 2020 California Silverado Fire on pyrogenic carbon (PyC) deposits using nitrogen and carbon isotopes as proxies. While the results showed significant variability in δ¹⁵N, δ¹³C, total carbon, and total nitrogen across sites, they did not support the hypothesis that wildfire increases δ¹⁵N while keeping δ¹³C constant, emphasizing the need for location-based controls when using δ¹⁵N to track PyC.
Read More...Modelling effects of alkylamines on sea salt aerosols using the Extended Aerosols and Inorganics Model

With monitoring of climate change and the evolving properties of the atmosphere more critical than ever, the authors of this study take sea salt aerosols into consideration. These sea salt aerosols, sourced from the bubbles found at the surface of the sea, serve as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and are effective for the formation of clouds, light scattering in the atmosphere, and cooling of the climate. With amines being involved in the process of CCN formation, the authors explore the effects of alkylamines on the properties of sea salt aerosols and their potential relevance to climate change.
Read More...The Dependence of CO2 Removal Efficiency on its Injection Speed into Water
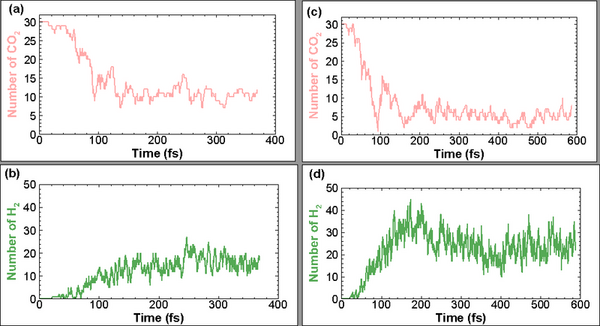
Recent research confirms that climate change, driven by CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels, poses a significant threat to humanity. In response, authors explore methods to remove CO2 from the atmosphere, including breaking its molecular bonds through high-speed collisions.
Read More...Testing Various Synthetic and Natural Fiber Materials for Soundproofing
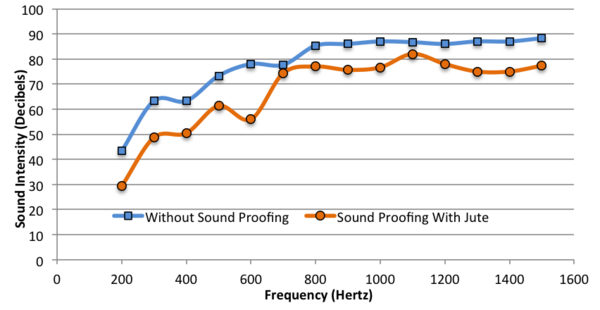
Noise pollution negatively impacts the health and behavioral routines of humans and other animals, but the production of synthetic sound-absorbing materials contributes to harmful gas emissions into the atmosphere. The authors of this paper investigated the effectiveness of environmentally-friendly, cheap natural-fiber materials, such as jute, as replacements for synthetic materials, such as gypsum and foam, in soundproofing.
Read More...Temperature and Precipitation Responses to a Stratospheric Aerosol Geoengineering Experiment Using the Community Climate System Model 4
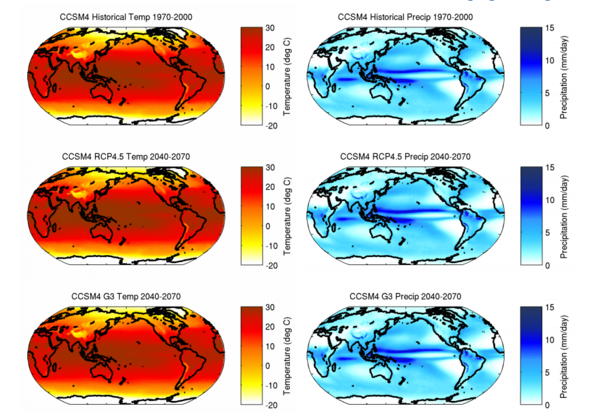
We are changing our environment with steadily increasing carbon dioxide emissions, but we might be able to help. The authors here use a computer program called Community Climate System Model 4 to predict the effects of spraying small particles into the atmosphere to reflect away some of the sun's rays. The software predicts that this could reduce the amount of energy the Earth's atmosphere absorbs and may limit but will not completely counteract our carbon dioxide production.
Read More...Correlation of Prominent Intelligence Type & Coworker Relations

Ashley Moulton & Joseph Rasmus investigate 9 controversial categories of intelligence as predicted by Multiple Intelligence Theory, originally proposed in the mid-1980s. By collecting data from 56 participants, they record that there may not actually be a correlation between these categorical types when it comes to workplace atmosphere and project efficiency.
Read More...Measuring the efficiency of greenhouse gases to absorb heat

In the age of global warming, these authors studied which of the four major greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide) change the most with increased temperature.
Read More...Use of drone with sodium hydroxide carriers to absorb carbon dioxide from ambient air
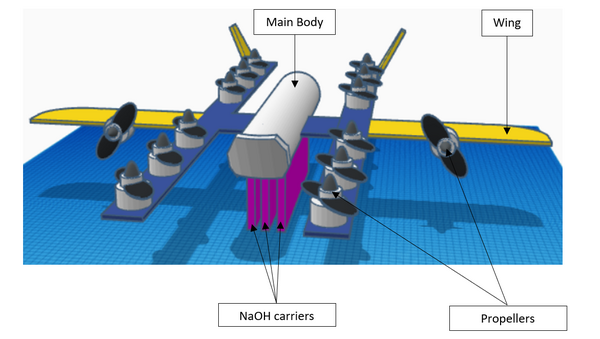
In this study, the authors address the current climate concern of high CO2 levels by testing solid forms of hydroxide for CO2 reduction and designing a drone to fly it in ambient air!
Read More...