
In this study, the authors surveyed a number of students in Singapore to determine how their experiences changed after the implementation of home-based learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read More...Psychosocial impact of home-based learning among students during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Singapore

In this study, the authors surveyed a number of students in Singapore to determine how their experiences changed after the implementation of home-based learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read More...Misconceptions regarding heart disease are prevalent among american adults and minors
In this study, the authors created a survey to assess misconceptions and knowledge deficits regarding cardiovascular diseases exist among US adults and minors.
Read More...The relationship between macroinvertebrates, water quality, and the health of Stevens Creek
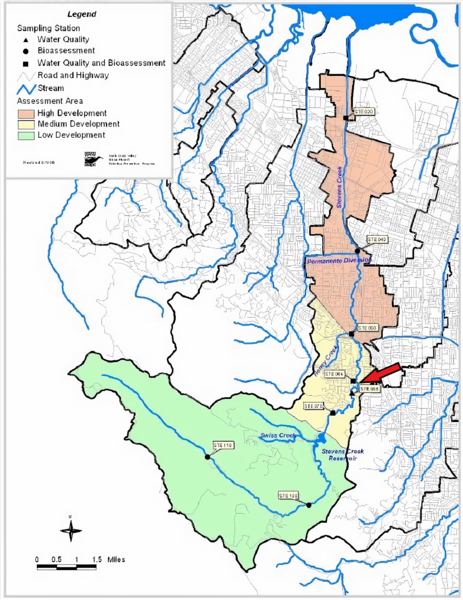
Stevens Creek, which flows through Santa Clara County in California, provides a crucial habitat for federally designated threatened steelhead trout, with a portion of the trout’s diet being dependent on the presence and abundance of macroinvertebrates that inhabit the creek. In this article, the authors investigate how the water chemistry within the creek was associated with the abundance and diversity of macroinvertebrates, and subsequently the creek’s health. They conduct qualitative analysis of macroinvertebrates and water quality to obtain a general understanding of the health of Stevens Creek.
Read More...Computational Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) of Berberine Analogs in Double-Stranded and G-Quadruplex DNA Binding Reveals Both Position and Target Dependence
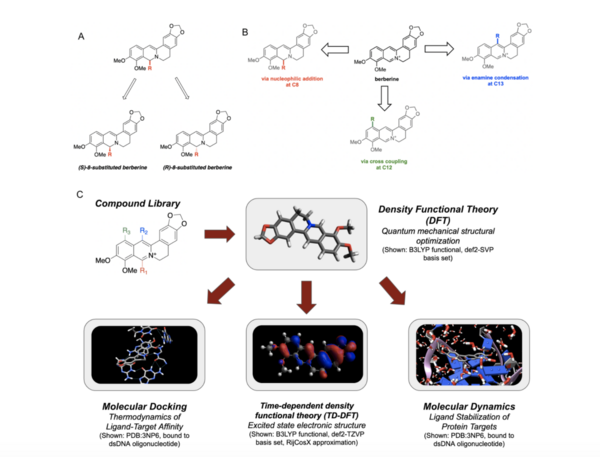
Berberine, a natural product alkaloid, and its analogs have a wide range of medicinal properties, including antibacterial and anticancer effects. Here, the authors explored a library of alkyl or aryl berberine analogs to probe binding to double-stranded and G-quadruplex DNA. They determined that the nature of the substituent, the position of the substituent, and the nucleic acid target affect the free energy of binding of berberine analogs to DNA and G-quadruplex DNA, however berberine analogs did not result in net stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA.
Read More...Estimation of Reproduction Number of Influenza in Greece using SIR Model
In this study, we developed an algorithm to estimate the contact rate and the average infectious period of influenza using a Susceptible, Infected, and Recovered (SIR) epidemic model. The parameters in this model were estimated using data on infected Greek individuals collected from the National Public Health Organization. Our model labeled influenza as an epidemic with a basic reproduction value greater than one.
Read More...Effects of Common Pesticides on Population Size, Motor Function, and Learning Capabilities in Drosophilia melanogaster

In this study, the authors examined the effects of commonly used pesticides (metolachlor, glyphosate, chlorpyrifos, and atrazine) on population size, motor function, and learning in Drosophila melanogaster.
Read More...Astragalus membranaceus Root Concentration and Exposure Time: Role in Heat Stress Diminution in C. elegans

In this study, the authors investigated the biological mechanism underlying the actions of a traditional medicinal plant, Astragalus membranaceus. Using C. elegans as an experimental model, they tested the effects of AM root on heat stress responses. Their results suggest that AM root extract may enhance the activity of endogenous pathways that mediate cellular responses to heat stress.
Read More...Examining Heat Recovery from Electric Light Bulbs Using Thermoelectric Generators
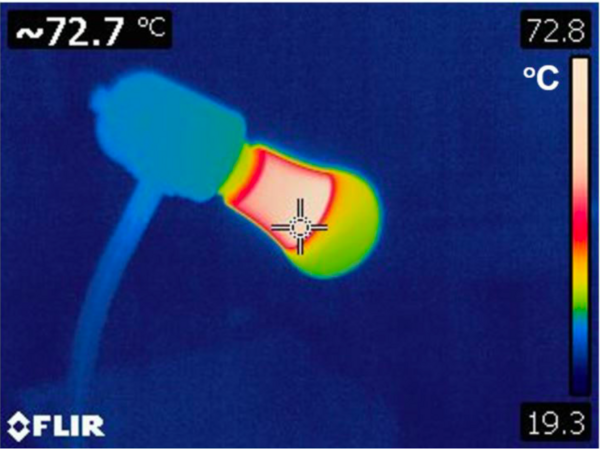
Here the author investigates how much heat energy is output and recovered from a conventional electric light bulb.
Read More...Correlations between Gray-White Matter Contrast in Prefrontal Lobe Regions and Cognitive Set-Shifting in Healthy Adults
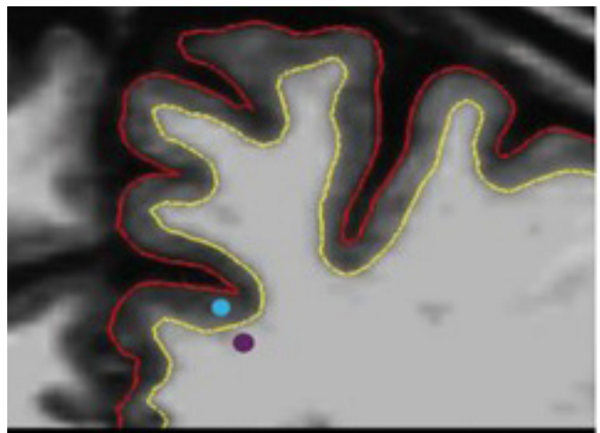
This study uses neuroimaging to investigate cognitive set-shifting, a type of executive function that involves shifting from one task to another. This study tested whether cortical gray-white matter contrast in subregions of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) was associated with set-shifting abilities in adults.
Read More...Molecular Alterations in a High-Fat Mouse Model Before the Onset of Diet–Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most prevalent chronic liver diseases worldwide, but there are few studied warning signs for early detection of the disease. Here, researchers study alterations that occur in a mouse model of NAFLD, which indicate the onset of NAFLD sooner. Earlier detection of diseases can lead to better prevention and treatment.
Read More...