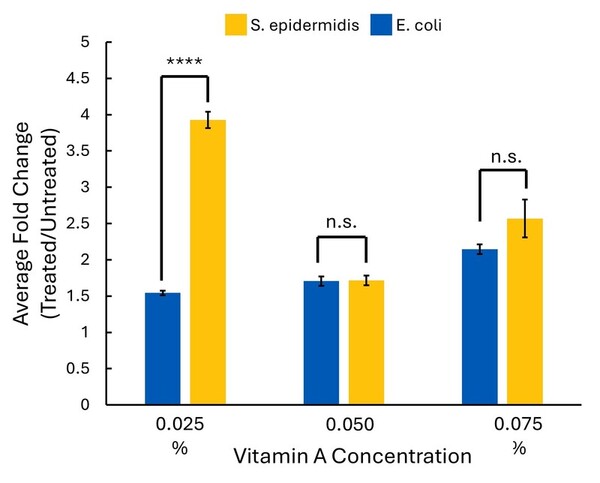
The authors looked at the impact of vitamin A (retinol) on growth of S. epidermidis (most abundant bacterium on the skin) and E. coli (found in the gut microbiome, but not on the skin).
Read More...Growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli when exposed to anti-acne vitamin A

The authors looked at the impact of vitamin A (retinol) on growth of S. epidermidis (most abundant bacterium on the skin) and E. coli (found in the gut microbiome, but not on the skin).
Read More...The Dependence of CO2 Removal Efficiency on its Injection Speed into Water
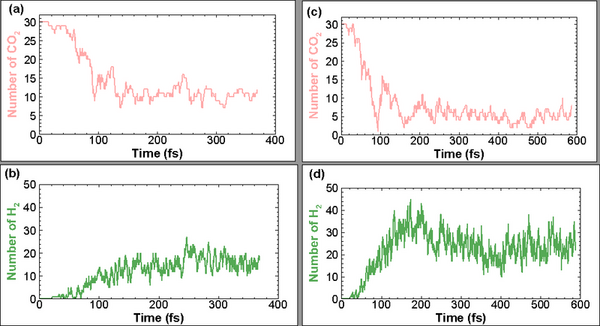
Recent research confirms that climate change, driven by CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels, poses a significant threat to humanity. In response, authors explore methods to remove CO2 from the atmosphere, including breaking its molecular bonds through high-speed collisions.
Read More...Calculating the dynamic viscosity of a fluid using image processing of a falling ball
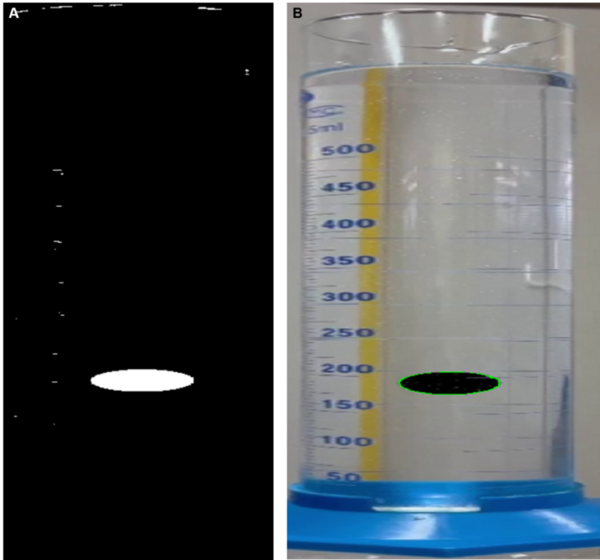
The authors measure changes in the viscosity of glycerol with increasing temperature using the falling ball approach.
Read More...A chemical and overwintering honey bee apiary field study comparing new and expired amitraz miticide

In this study, the authors test the longevity of a anti-mite compound, amitraz, in commercially-sold strips and the age-dependent efficacy of these strips in preventing honey bee colony collapse by ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor.
Read More...Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis of seven wisconsin biosolids

The authors analyzed biosolids from five Wisconsin wastewater treatment plants and suggest using KBr pellet FTIR as a simple and rapid method to start characterizing P species in biosolids.
Read More...Factors Influencing Muon Flux and Lifetime: An Experimental Analysis Using Cosmic Ray Detectors
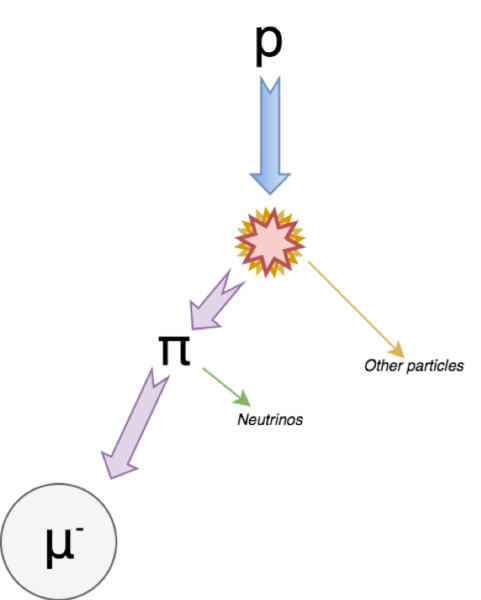
Muons, one of the fundamental elementary particles, originate from the collision of cosmic rays with atmospheric particles and are also generated in particle accelerator collisions. In this study, Samson et al analyze the factors that influence muon flux and lifetime using Cosmic Ray Muon Detectors (CRMDs). Overall, the study suggests that water can be used to decrease muon flux and that scintillator orientation is a potential determinant of the volume of data collected in muon decay studies.
Read More...Threshold Frequency of a Bubble is Positively Correlated to the Density of the Surrounding Fluid

In this article the authors explore the peculiar behavior of sinking bubbles. By investigating the relationship between the viscosity of a fluid and the the formation of stationary bubbles, they identify why bubbles behave differently between in different fluids.
Read More...Variation in Caffeine Concentration Among Different Weight Loss Supplements Containing Green Tea and Green Coffee Extracts
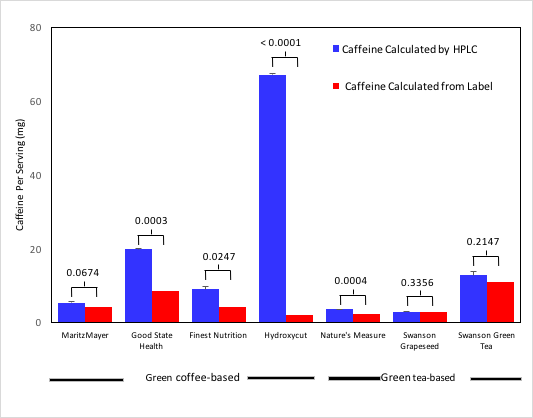
Many weight loss supplements contain the stimulant caffeine, but do not disclose the amount. Here, authors measure and compare the amount of caffeine in different dietary supplements. This research gives consumers better understanding of the impact natural supplements may have on their health.
Read More...Development of Two New Efficient Means of Wastewater Treatment
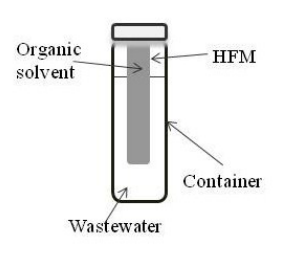
The water we use must be treated and cleaned before we release it back into the environment. Here, the authors investigate two new techniques for purifying dissolved impurities from waste water. Their findings may give rise to more cheaper and more efficient water treatment and help keep the planet greener.
Read More...What is the optimal fuel for space flight? Efficiency, cost, and environmental impact

Here, the authors sought to investigate the efficiency, cost, and environmental impact of several possible propellants that are or could be used for space flight. By deriving three novel equations, they identified harm, energy, and cost scores for each fuel, suggesting that considering each factor will be essential to the ongoing growth of the space industry.
Read More...