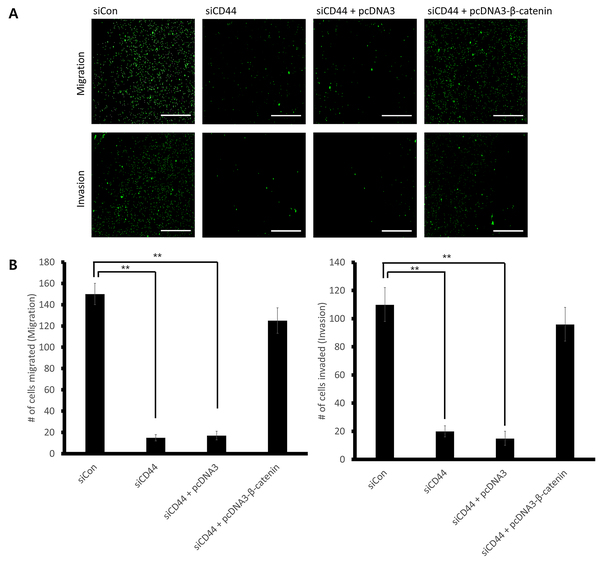
Collisions of heavy ions, such as muons result in jets and noise. In high-energy particle physics, researchers use jets as crucial event-shaped observable objects to determine the properties of a collision. However, many ionic collisions result in large amounts of energy lost as noise, thus reducing the efficiency of collisions with heavy ions. The purpose of our study is to analyze the relationships between properties of muons in a dimuon collision to optimize conditions of dimuon collisions and minimize the noise lost. We used principles of Newtonian mechanics at the particle level, allowing us to further analyze different models. We used simple Python algorithms as well as linear regression models with tools such as sci-kit Learn, NumPy, and Pandas to help analyze our results. We hypothesized that since the invariant mass, the energy, and the resultant momentum vector are correlated with noise, if we constrain these inputs optimally, there will be scenarios in which the noise of the heavy-ion collision is minimized.
Read More...