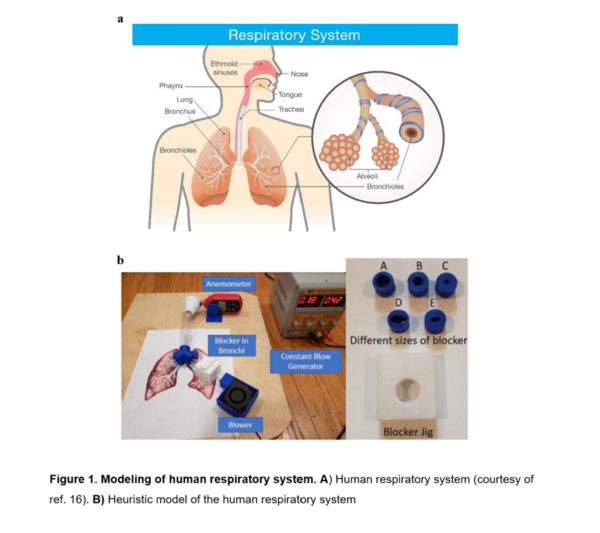
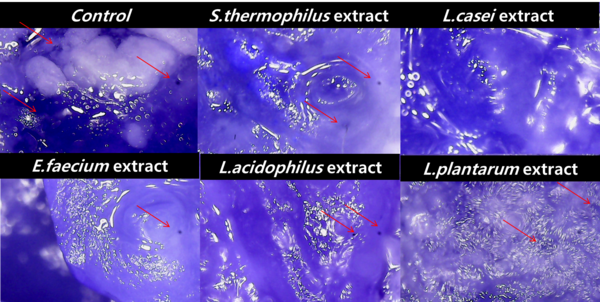
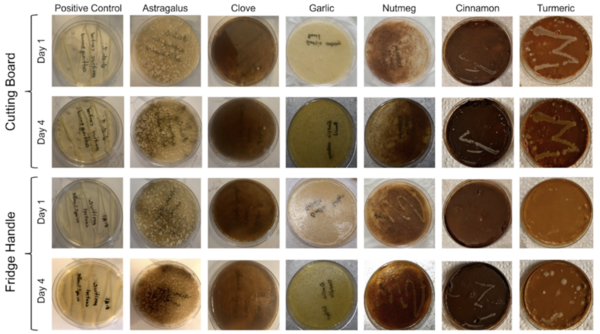
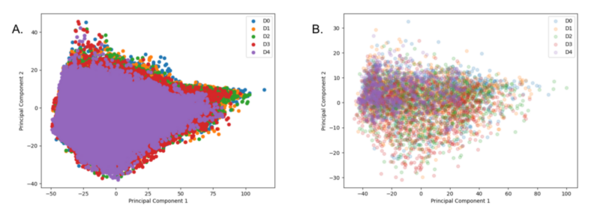
Mosquito-borne diseases are a major issue across the world, and the objective for this project was to determine the characteristics that make some communities more susceptible to these diseases than others. The authors identified and studied characteristics that make communities susceptible to mosquito-borne diseases, including water in square miles, average temperature, population, population density, and poverty rates per county. They found that the population of a county is the best indicator of the prevalence of mosquito-borne diseases.
Read More...