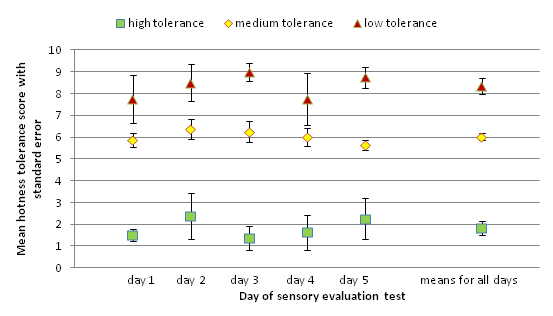
Cuisine with hot chili peppers can be tasty, but sometimes painful to consume because of the burning sensations caused by the capsaicin molecule. The authors wanted to find the palate reliever that decreases the burning sensation of capsaicin the most by testing water, soft drink, olive oil, milk, and ice-cream as possible candidates. The authors hypothesized that olive oil would be the best palate reliever as it is non-polar like the capsaicin molecule. The authors surveyed 12 panelists with low, medium, and high spice tolerances and found that across all levels of spice tolerance, milk and ice-cream were the best palate relievers and soft drink the worst.
Read More...