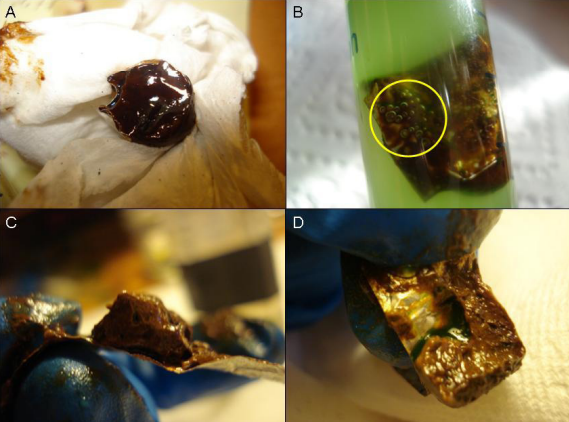
Ecological corridors are geographic features designated to allow the movement of wildlife populations between habitats that have been fragmented by human landscapes. Corridors can be a pivotal aspect in wildlife conservation because they preserve a suitable habitat for isolated populations to live and intermingle. Here, two students simulate the effect of introducing a safety corridor for cheetahs, based on real tracking data on cheetahs in Namibia.
Read More...