The use of computer vision to differentiate valley fever from lung cancer via CT scans of nodules
(1) Stockdale High School, (2) California State University
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-247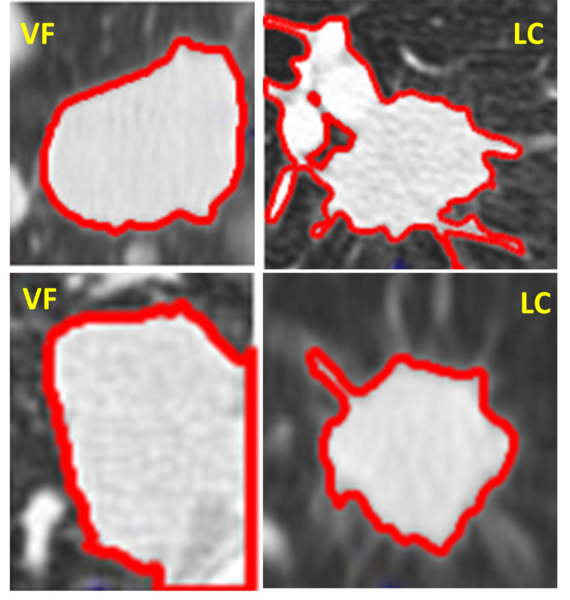
Pulmonary diseases, notably lung cancer and valley fever, pose significant health risks. Therefore, a swift and accurate diagnostic tool is imperative. This study sought to harness advanced technologies, integrating computer vision techniques with computed tomography (CT) scans, to differentiate between lung cancer and valley fever, thereby enhancing diagnostic precision. We hypothesized that the MATLAB-based software tool developed would discern minute and distinct features of lung nodules specific to either lung cancer or valley fever with more precision than traditional diagnostics. Upon use of Otsu's thresholding and object size filtering, distinct morphological features were extracted from binary versions of the images. The MATLAB-based software consistently detected and differentiated lung cancer and valley fever based on the nodules' features, such as solidity, extent, and roundedness, among others. While size wasn't a consistent indicator as per previous studies, features like solidity showed great contrast between the distinct images. Overall, the software demonstrated promising potential in providing features to differentiate between two critical pulmonary diseases. However, a future study is needed with a larger number of images to further validate and refine the prediction algorithm prototype developed in this work, ensuring its accuracy for potential implementation in clinical settings. Once the technique is fully developed, it could reduce the chances of human error and expedite early detection and intervention. Future enhancements may incorporate other imaging modalities, promoting diagnostic capabilities. The study underlines the transformative role of machine learning-based analysis of CT scans in revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics.
This article has been tagged with: