The authors looked at how soil temperature changes with fire to develop a sensor system that could aid in earlier detection of fires.
Read More...Browse Articles
Quantifying coliform bacteria in ground beef to evaluate food safety guidelines
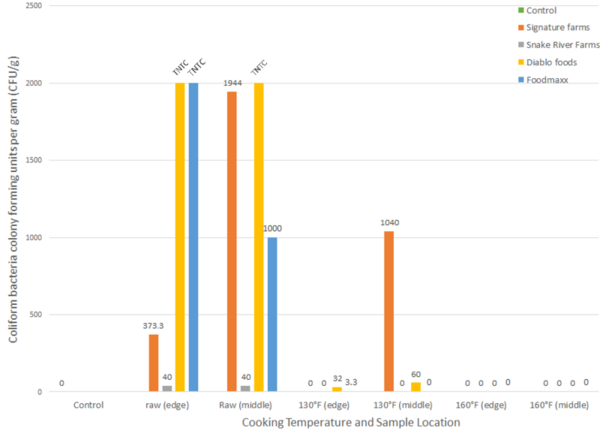
The authors looked at the presence of coliform bacteria present in ground beef after cooking it various CDC standards. They found that no coliform bacteria was present when CDC guidelines for cooking ground beef were properly followed.
Read More...Heat conduction: Mathematical modeling and experimental data
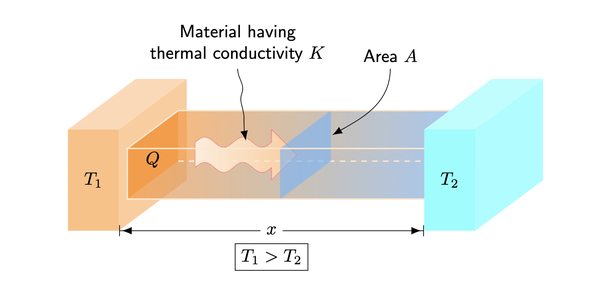
In this experiment, the authors modify the heat equation to account for imperfect insulation during heat transfer and compare it to experimental data to determine which is more accurate.
Read More...PCR technology for screening genetically modified soybeans

In order to determine whether unmarked soybeans in the market were genetically modified crops, the authors developed a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) screen for DNA lectin.
Read More...A novel bioreactor system to purify contaminated runoff water
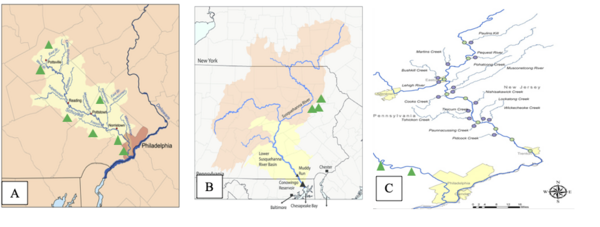
In this study, the authors engineer a cost-effective and bio-friendly water purification system using limestone, denitrifying bacteria, and sulfate-reducing bacteria. They evaluated its efficacy with samples from Eastern PA industrial sites.
Read More...Investigation of Bunsen-type Premixed Flame Response to Acoustic Excitation: Temperature and Flame Profile
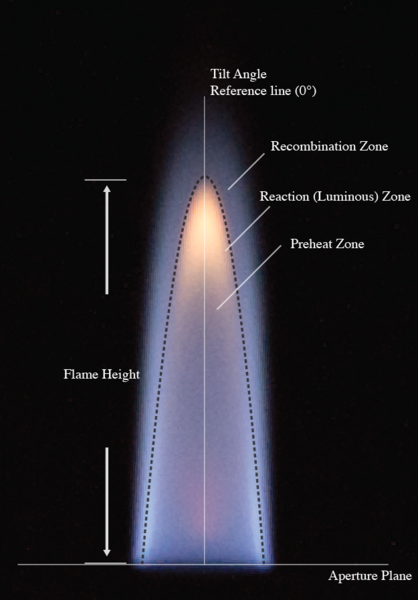
Here, authors characterize how different acoustics affect the properties of a Bunsen-type flame.
Read More...The Effect of Cooking Method on the Amount of Fat in an Egg
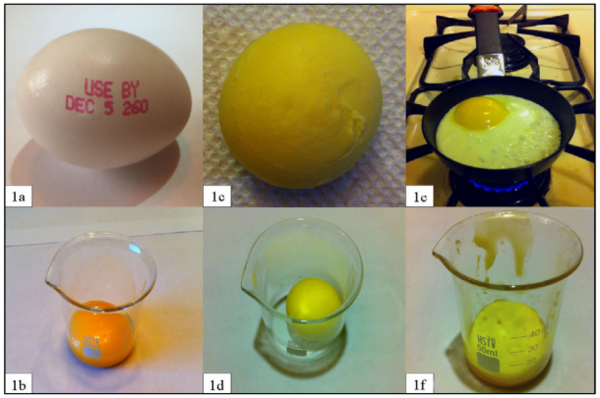
Fat can be chemically altered during cooking through a process called lipid oxidation, which can have a negative impact on health. In this study, the authors measured the extracted fat in raw, fried and hard-boiled eggs and found that cooking eggs to a higher temperature resulted in a lower amount of extracted fat, indicating a greater amount of oxidized fat.
Read More...Temperature and Precipitation Responses to a Stratospheric Aerosol Geoengineering Experiment Using the Community Climate System Model 4
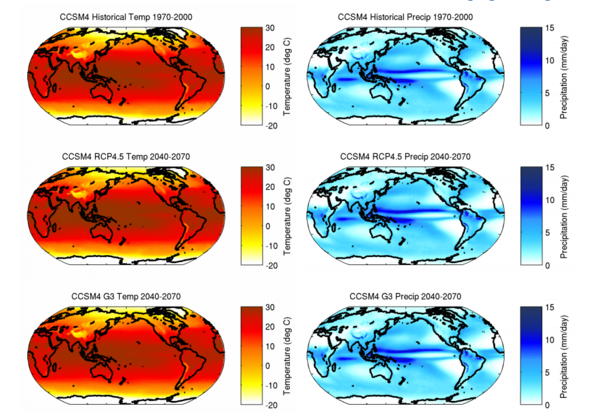
We are changing our environment with steadily increasing carbon dioxide emissions, but we might be able to help. The authors here use a computer program called Community Climate System Model 4 to predict the effects of spraying small particles into the atmosphere to reflect away some of the sun's rays. The software predicts that this could reduce the amount of energy the Earth's atmosphere absorbs and may limit but will not completely counteract our carbon dioxide production.
Read More...Pressure and temperature influence the efficacy of metal-organic frameworks for carbon capture and conversion
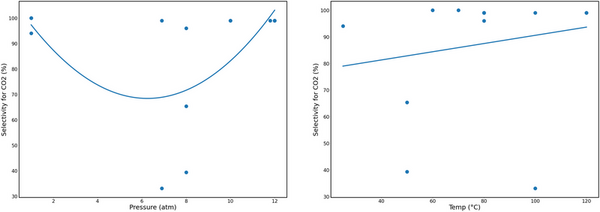
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising new nanomaterials for use in the fight against climate change that can efficiently capture and convert CO2 to other useful carbon products. This research used computational models to determine the reaction conditions under which MOFs can more efficiently capture and convert CO2. In a cost-efficient manner, this analysis tested the hypothesis that pressure and temperature affect the efficacy of carbon capture and conversion, and contribute to understanding the optimal conditions for MOF performance to improve the use of MOFs for controlling greenhouse CO2 emissions.
Read More...Effects of Coolant Temperature on the Characteristics of Soil Cooling Curve
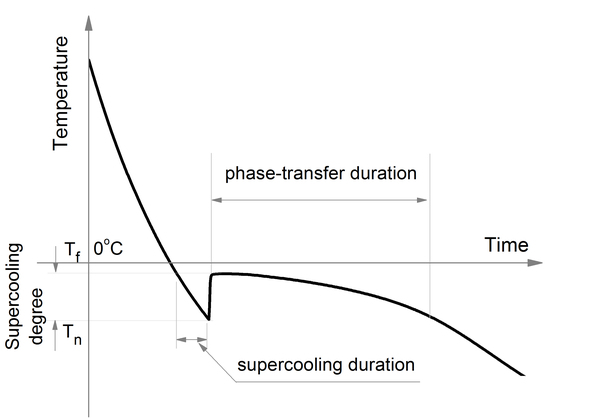
In this article, the authors investigate whether coolant temperature affects soil cooling curves of soil with otherwise identical properties. The coolant temperature is representative of environmental temperature, and the authors hypothesized that differences in this temperature would not affect the freezing temperature of soil. Their findings validated their hypothesis providing helpful information relevant to understanding how frost heaves happen and how to predict their occurrence more accurately.
Read More...