
In the age of global warming, these authors studied which of the four major greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide) change the most with increased temperature.
Read More...Measuring the efficiency of greenhouse gases to absorb heat

In the age of global warming, these authors studied which of the four major greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide) change the most with increased temperature.
Read More...The effect of the pandemic on the behavior of junior high school students

Here, seeking to understand how the COVID-19 pandemic affected the social interactions of junior high school students, the authors surveyed students, teachers, and parents. Contrary to their initial hypotheses, the authors found positive correlation between increased virtual contact during social isolation and in-person conflict and disregard for social norms after the pandemic. While the authors identified the limitations of their study, they suggest that further research into the effect of online interactions is becoming increasingly important.
Read More...The effect of nicotine and lead on neuron morphology, function, and ɑ-Synuclein levels in a C. elegans model
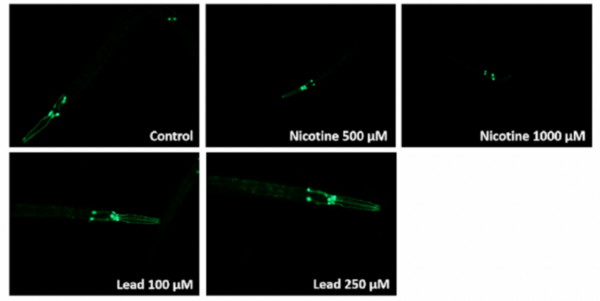
E-cigarettes are often considered a healthier alternative to traditional cigarettes. This team of high school authors investigated the impact of common e-cigarette compounds on C. elegans, and found a number of harmful effects ultimately resulting in injury and neuronal damage.
Read More...Uncovering mirror neurons’ molecular identity by single cell transcriptomics and microarray analysis
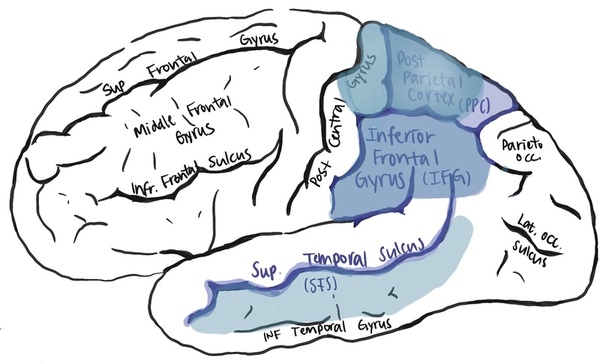
In this study, the authors use bioinformatic approaches to characterize the mirror neurons, which are active when performing and seeing certain actions. They also investigated whether mirror neuron impairment was connected to neural degenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders.
Read More...Different volumes of acetic acid affect the oxygen production of spinach leaves during photosynthesis
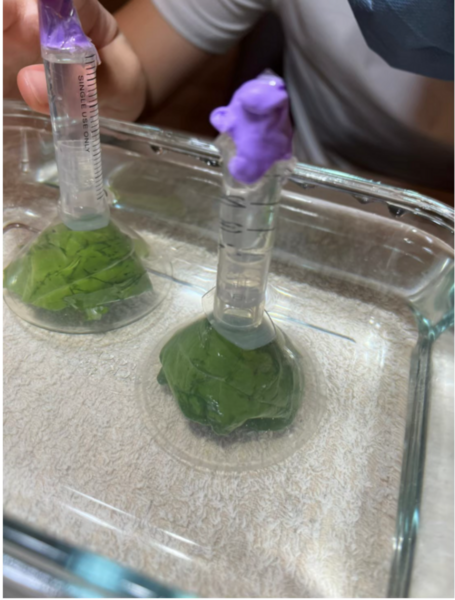

The burning of fossil fuels, leading to an increased amount of carbon emissions, is the main cause of acid rain. Acid rain affects the process of photosynthesis, which makes the topic valuable to investigate. Our group utilizes plants to further investigate the relationship between pH value and photosynthesis. In this experiment, our group hypothesized that rain with a lower pH will decrease the rate of photosynthesis, causing less oxygen to be produced in the reaction.
Read More...Distribution of prophages in the Streptococcus bacteria genus and their role in increasing host pathogenicity
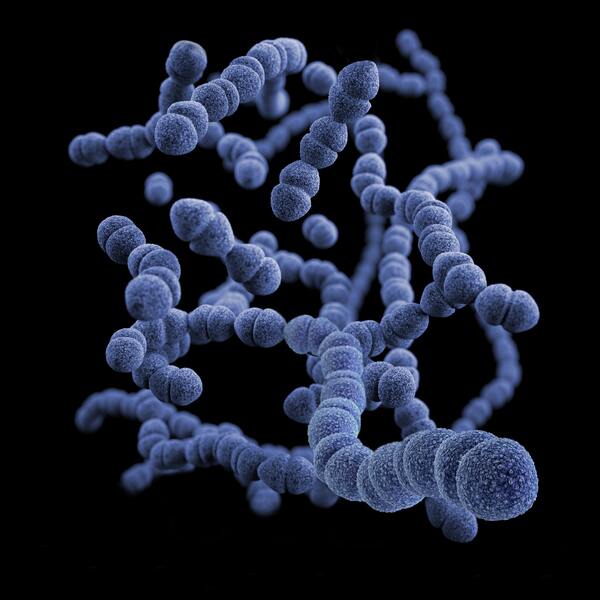
The authors investigated prophages present in Streptococcus bacteria that may increase their survival in different environments.
Read More...Pediatric probiotic culture survival study in acidic pH using an in vitro model
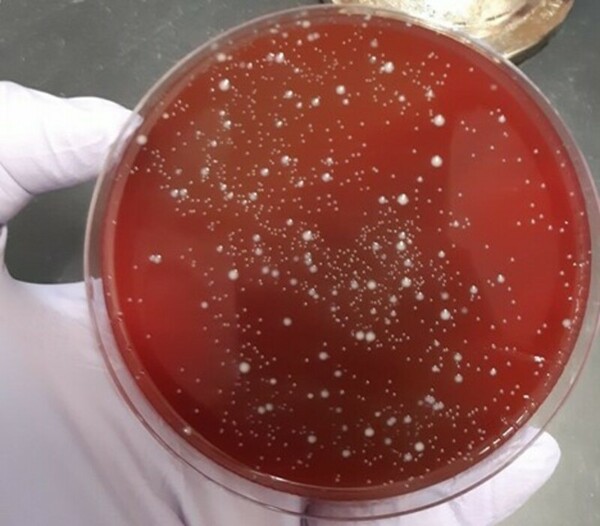
In this study, the authors investigate the effects of acidity on the survival of commercial probiotic Lovebug bacterial strains.
Read More...The novel function of PMS2 mutation on ovarian cancer proliferation
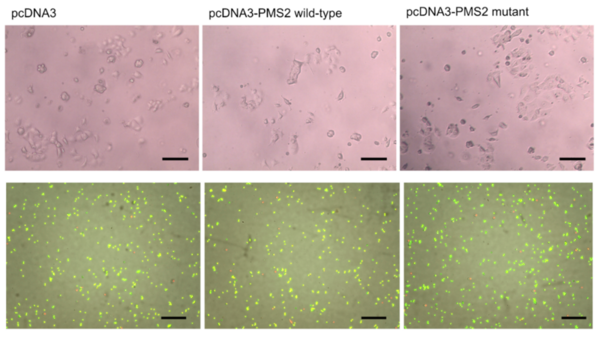
With disruption of DNA repair pathways pertinent to the timeline of cancer, thorough evaluation of mutations relevant to DNA repair proteins is crucial within cancer research. One such mutation includes S815L PMS2 - a mutation that results in significant decrease of DNA repair function by PMS2 protein. While mutation of PMS2 is associated with significantly increased colorectal and endometrial cancer risk, much work is left to do to establish the functional effects of the S815L PMS2 mutation in ovarian cancer progression. In this article, researchers contribute to this essential area of research by uncovering the tumor-progressive effects of the S815L PMS2 mutation in the context of ovarian cancer cell lines.
Read More...Myrtaceaes as antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
In this study, the authors test new antimicrobials by measuring the ability of extracts from Australian-native Myrtaceae species to induce death of two bacteria S. aureus and P. aeruginosa.
Read More...The impact of COVID-19 quarantine on physical activities in Basra, Iraq: A cross-sectional study

As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the authors noticed a change in the physical activity of many people, as well as a change in the type of physical activity they practice. Here, the authors used a cross-sectional survey of 150 participants from the province of Basra in Iraq. They found an overall decrease in the number of days of physical activity for participants along with an increasing proportion of at-home exercises compared to other activities that are performed inside sports clubs during the pandemic.
Read More...