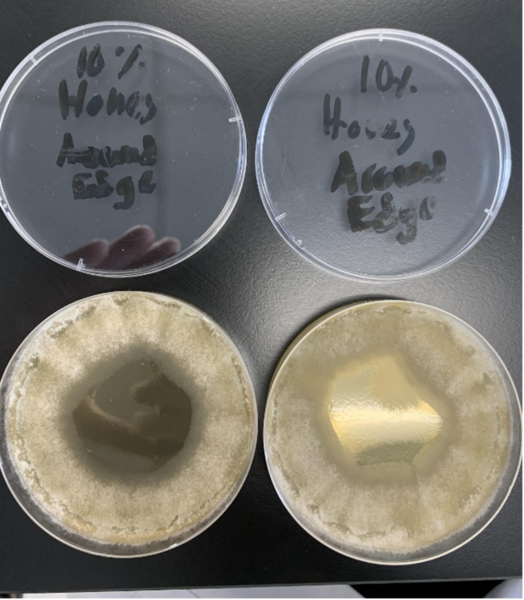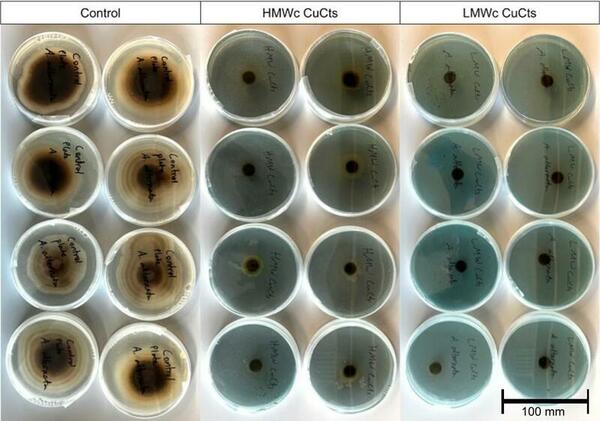
Pathogenic fungi such as Alternaria alternata (A. alternata) can decimate crop yields and severely limit food supplies when left untreated. Copper chitosan (CuCts) is a promising alternative fungicide for developing agricultural areas due to being inexpensive and nontoxic. We hypothesized that LMWc CuCts would exhibit greater fungal inhibition due to the beneficial properties of LMWc.
Read More...