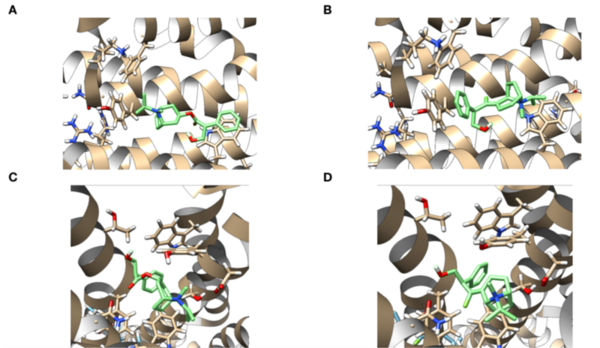
Anticholinergics are used in treating asthma, a chronic inflammation of the airways. These drugs block human M1 and M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, inhibiting bronchoconstriction. However, studies have reported complications of anticholinergic usage, such as exacerbated eosinophil production and worsened urinary retention. Modification of known anticholinergics using bioisosteric replacements to increase efficacy could potentially minimize these complications. The present study focuses on identifying viable analogs of anticholinergics to improve binding energy to the receptors compared to current treatment options. Glycopyrrolate (G), ipratropium (IB), and tiotropium bromide (TB) were chosen as parent drugs of interest, due to the presence of common functional groups within the molecules, specifically esters and alcohols. Docking score analysis via AutoDock Vina was used to evaluate the binding energy between drug analogs and the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. The final results suggest that G-A3, IB-A3, and TB-A1 are the most viable analogs, as binding energy was improved when compared to the parent drug. G-A4, IB-A4, IB-A5, TB-A3, and TB-A4 are also potential candidates, although there were slight regressions in binding energy to both muscarinic receptors for these analogs. By researching the effects of bioisosteric replacements of current anticholinergics, it is evident that there is a potential to provide asthmatics with more effective treatment options.
Read More...