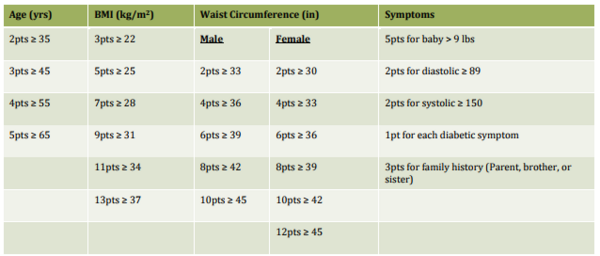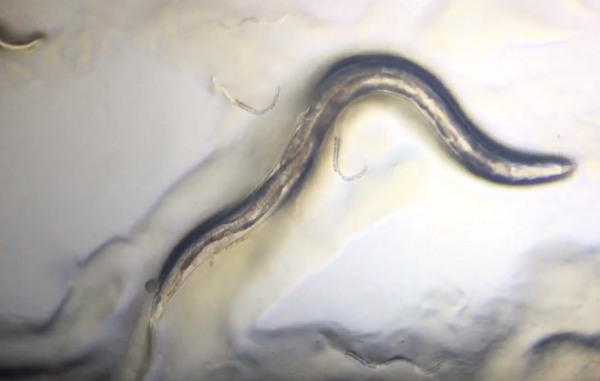
Kadıoğlu and Oğuzalp study the synergistic effects of Metformin and Captopril, two commonly prescribed drugs for type 2 diabetes and hypertension, respectively. Using C. elegans nematodes as a model system, the authors find that the nematodes decreased in average body length when exposed to Metformin or Captopril individually, but grew 11% in body length when both drugs were used together. Because C. elegans body size is regulated in part by the TGF-β signaling pathway, the authors suggest that synergistic effects of these two drugs may be modulating TGF-β activity, a previously uncharacterized phenomenon.
Read More...