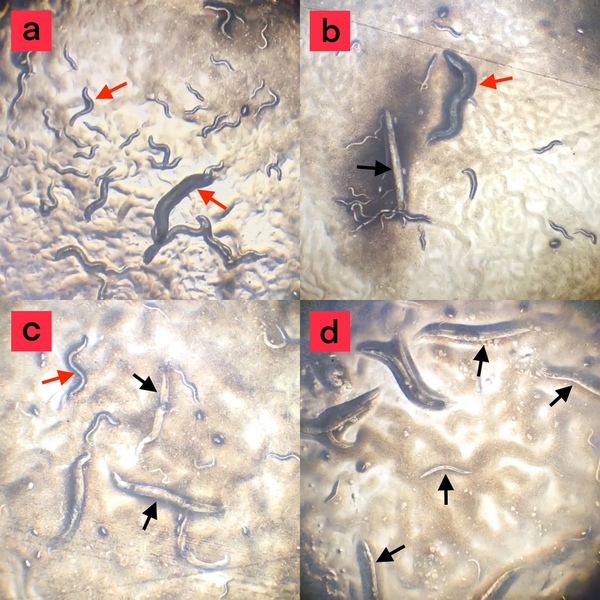
Caenorhabditis elegans xpa-1 and him-1 are orthologs of human XPA and human SMC1A, respectively. Mutations in the XPA are correlated with Xeroderma pigmentosum, a condition that induces hypersensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Alternatively, SMC1A mutations may lead to Cornelia de Lange Syndrome, a multi-organ disorder that makes patients more sensitive to UVinduced DNA damage. Both C. elegans genes have been found to be involved in protection against UV radiation, but their combined effects have not been tested when they are both knocked down. The authors hypothesized that because these genes are involved in separate pathways, the simultaneous knockdown of both of these genes using RNA interference (RNAi) in C. elegans will cause them to become more sensitive to UV radiation than either of them knocked down individually. UV protection was measured via the percent survival of C. elegans post 365 nm and 5.4x10-19 joules of UV radiation. The double xpa-1/him-1 RNAi knockdown showed a significantly reduced percent survival after 15 and 30 minutes of UV radiation relative to wild-type and xpa-1 and him-1 single knockdowns. These measurements were consistent with their hypothesis and demonstrated that xpa-1 and him-1 genes play distinct roles in resistance against UV stress in C. elegans. This result raises the possibility that the xpa-1/him-1 double knockdown could be useful as an animal model for studying the human disease Xeroderma pigmentosum and Cornelia de Lange Syndrome.
Read More...