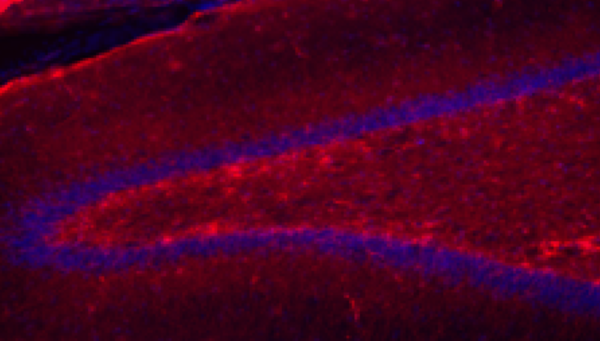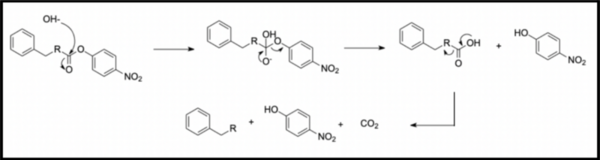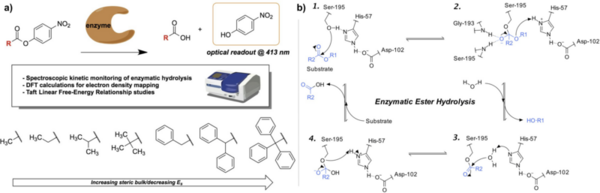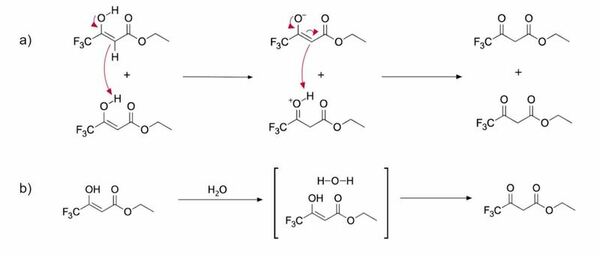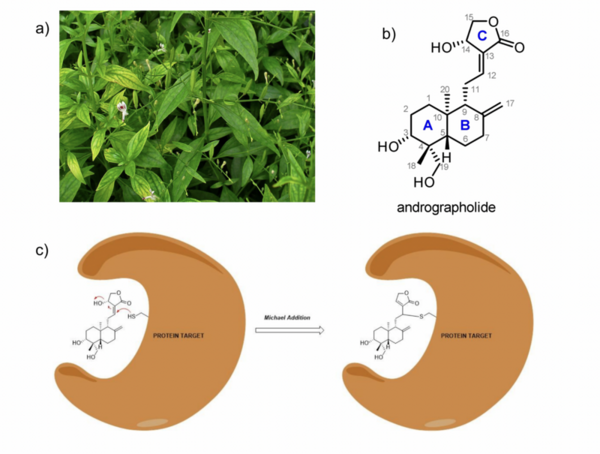
Here, based on the identification of androgapholide as a potential therapeutic treatment against cancer, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, and multiple sclerosis, due to its ability to inhibit a signaling pathway in immune system function, the authors sought ways to optimize the natural product human systems by manipulating its chemical structure. Through the semisynthesis of a natural product along with computational studies, the authors developed an understanding of the kinetic mechanisms of andrographolide and semisynthetic analogs in the context of Michael additions.
Read More...