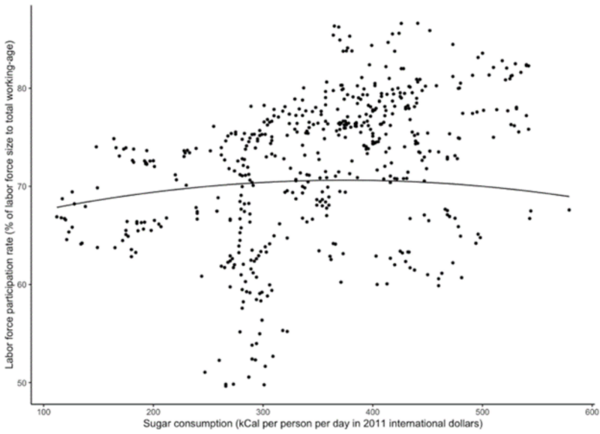
In this article the authors look at sugar consumption and the relationship to productivity in the work/labor force.
Read More...A spatiotemporal analysis of OECD member countries on sugar consumption and labor force participation

In this article the authors look at sugar consumption and the relationship to productivity in the work/labor force.
Read More...Are Asian foods healthier than Western foods: Evidence collected from St. Louis area grocery stores
The authors compare nutritional content of foods found in Western versus Asian grocery stores to determine whether one cultural diet is healthier than the other.
Read More...Building deep neural networks to detect candy from photos and estimate nutrient portfolio

The authors use pictures of candy wrappers and neural networks to improve nutritional accuracy of diet-tracking apps.
Read More...Nature’s reset: The effect of native and invasive plant forage on honey bee nutrition and survival
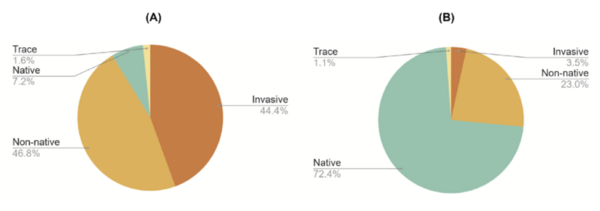
The authors looked at survival of honey bees over the winter in regards to native and invasive plant availability. They found that native plants provided greater survivability and overall health compared to environments where there was an abundance of invasive plants.
Read More...Who is at Risk for a Spinal Fracture? – A Comparative Study of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
One common age-related health problem is the loss of bone mineral density (BMD), which can lead to a variety of negative health outcomes, including increased risk of spinal fracture. In this study, the authors investigate risk factors that may be predictive of an individual's risk of spinal fracture. Their findings provide valuable information that clinicians can use in patient evaluations.
Read More...The Effect of Ultraviolet Radiation and the Antioxidant Curcumin on the Longevity, Fertility, and Physical Structure of Drosophila melanogaster: Can We Defend Our DNA?
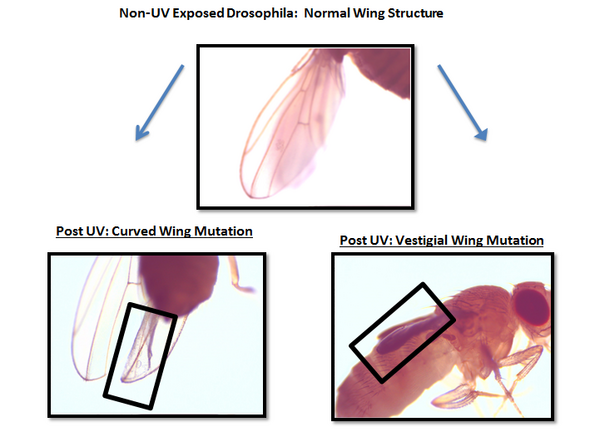
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is known to alter DNA structure and impair cellular function in all living organisms. In this study, Lateef et al examine the effects of UV radiation to determine whether antioxidant-enriched nutrition can combat the potential deleterious effects of UV radiation on Drosophila melanogaster. They found that UVB (320nm) radiation caused a 59% decrease in the Drosophila lifespan and mutagenic effects on flies' physical appearance, but did not significantly affect fertility. Curcumin significantly prolonged lifespan and enhanced fertility for both UV- and non-UV-exposed flies. The research demonstrates the positive potential of natural antioxidants as weapons against radiation-induced diseases including cancer.
Read More...How are genetically modified foods discussed on TikTok? An analysis of #GMOFOODS

Here, the authors investigated engagement with #GMOFOODS, a hashtag on TikTok. They hypothesized that content focused on the negative effects of genetically modified organisms would receive more interaction driven by consumers. They found that the most common cateogry focused on the disadvantages of GMOs related to nutrition and health with the number of views determining if the video would be provided to users.
Read More...A comparative study of food labels in the United States and India: Adherence to Codex Alimentarius guidelines
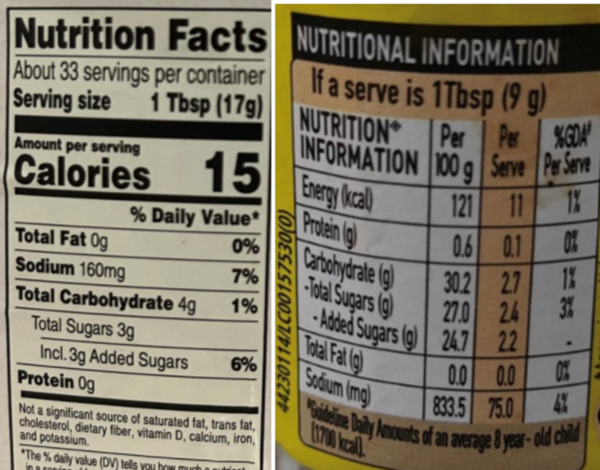
This study investigated how well food labels from 280 different brands across multiple food and drink categories in India and the US adhered to recommended nutritional labeling standards as outlined by the Codex Alimentarius.
Read More...Association of depression and suicidal ideation among adults with the use of H2 antagonists
In this study, the authors investigate associations between use of histamine H2 receptor antagonists and suicidal ideation in different age groups.
Read More...FRUGGIE – A Board Game to Combat Obesity by Promoting Healthy Eating Habits in Young Children

The authors created a board game to teach young children about healthy eating habits to see whether an interactive and family-oriented method would be effective at introducing and maintaining a love for fruits and veggies. Results showed that children developed a liking for fruits and vegetables, and none regressed. Half maintained their level of enjoyment for fruits and vegetables during the research period, while the other half had a positive increase. The results show that a simple interactive game can shape how young children relate to food and encourage them to maintain healthy habits.
Read More...