
In this study, the impact of shutting down schools on the emotional aspects of high school students was analyzed using survey responses.
Read More...COVID-19 pandemic impact on emotional aspects of high school students

In this study, the impact of shutting down schools on the emotional aspects of high school students was analyzed using survey responses.
Read More...The knowledge and perception of opioid abuse and its long-term effects among high schoolers
Due to the susceptibility of adolescent age groups to opioid misuse, here the authors sought to determine if there was a difference in the perception and knowledge between 9th and 12th graders regarding the opioid crisis. An educational intervention trial was done with the 9th graders and surveys were used to identify its effects. Although the authors acknowledge a small sample size, their results suggest that their are gaps within the knowledge of adolescents in regards to opioid misuse and its long-term effects that could be addressed with further education.
Read More...A study of South Korean international school students: Impact of COVID-19 on anxiety and learning habits
.jpg)
In this study, the authors investigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on South Korean international school students' anxiety, well being and their learning habits.
Read More...Misconceptions regarding heart disease are prevalent among american adults and minors
In this study, the authors created a survey to assess misconceptions and knowledge deficits regarding cardiovascular diseases exist among US adults and minors.
Read More...The impact of Red 40 artificial food dye on the heart rate of Daphnia magna
.jpg)
In this study, potential physiological effects of Red 40 food dye, found in many different food products, are tested using Daphnia magna, a small freshwater crustacean.
Read More...A comparative analysis of machine learning approaches for prediction of breast cancer
Machine learning and deep learning techniques can be used to predict the early onset of breast cancer. The main objective of this analysis was to determine whether machine learning algorithms can be used to predict the onset of breast cancer with more than 90% accuracy. Based on research with supervised machine learning algorithms, Gaussian Naïve Bayes, K Nearest Algorithm, Random Forest, and Logistic Regression were considered because they offer a wide variety of classification methods and also provide high accuracy and performance. We hypothesized that all these algorithms would provide accurate results, and Random Forest and Logistic Regression would provide better accuracy and performance than Naïve Bayes and K Nearest Neighbor.
Read More...Caffeine: Does Drinking Coffee Alter Performance and RPE Levels of a Teenage Athlete in both Aerobic and Anaerobic Exercises?

Caffeine is widely consumed across the globe and is most appreciated for its effects as a stimulant. Here the authors investigate whether caffeine consumption affects performance during endurance or strength training. Their results suggest that caffeine consumption enhances endurance training, but not strength training.
Read More...Honey Bee Pollen in Allergic Rhinitis Healing

The most common atopic disease of the upper respiratory tract is allergic rhinitis. It is defined as a chronic inflammatory condition of nasal mucosa due to the effects of one or more allergens and is usually a long-term problem. The purpose of our study was to test the efficiency of apitherapy in allergic rhinitis healing by the application of honey bee pollen. Apitherapy is a branch of alternative medicine that uses honey bee products. Honey bee pollen can act as an allergen and cause new allergy attacks for those who suffer from allergic rhinitis. Conversely, we hoped to prove that smaller ingestion of honey bee pollen on a daily basis would desensitize participants to pollen and thus reduce the severity of allergic rhinitis.
Read More...Trajectories Between Cigarette Smoking and Electronic Nicotine Delivery System Use Among Adults in the U.S.

In this study, the authors characterized the trends of cigarette use amongst people who do and don't use electronic nicotine delivery systems (or ENDS). This was done to help determine if the use of ENDS is aiding in helping smokers quit, as the data on this has been controversial. They found that use of ENDS among people either with or without previous cigarette usage were more likely to continue using cigarettes in the future. This is important information contributing to our understanding of ways to effectively (and not effectively) reduce cigarette use.
Read More...Behavioral Longevity: The Impact of Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and Obesity on Life Expectancy
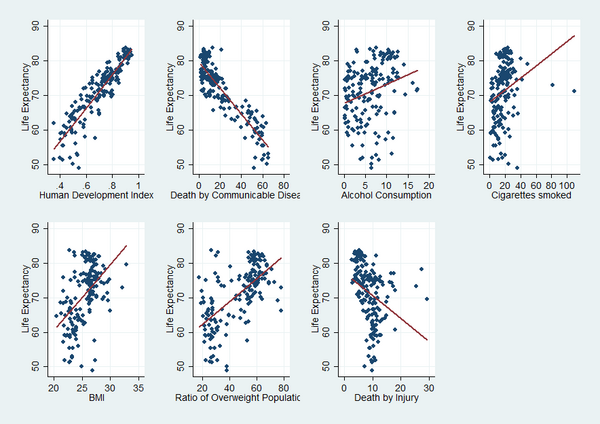
In this article, the authors look into what is already known about the factor affecting longevity and determine the importance of behavioral factors including alcohol consumption, smoking, and obesity on longevity. The authors quantify data from over 150 countries and, interestingly, find that the impact each factor has on longevity is at least in part dependent on the country's economic development status. Overall, they conclude that an average person’s life expectancy can increase by more than 3 years if smoking and alcohol consumption is reduced by a half and weight is decreased by 10%.
Read More...