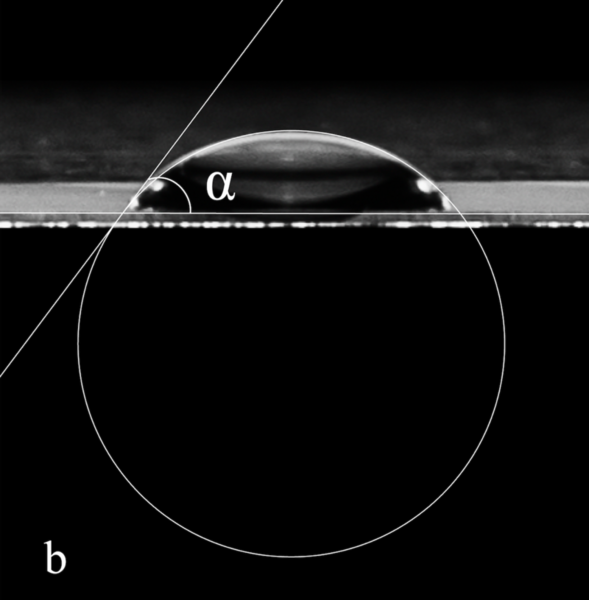
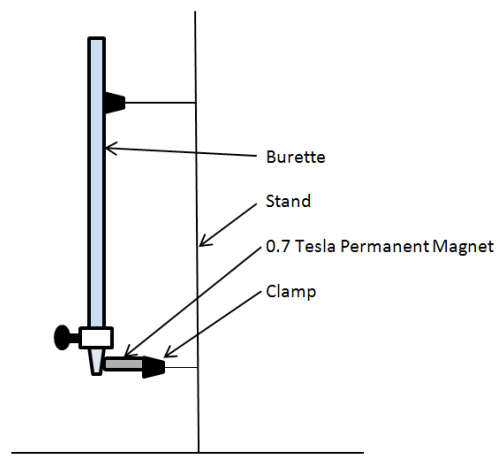
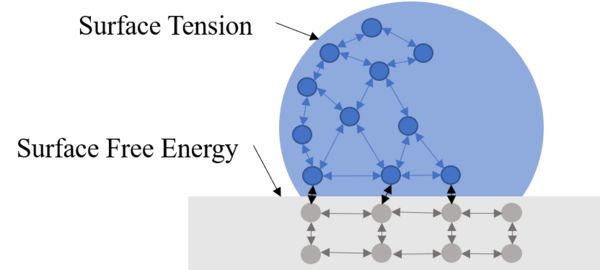
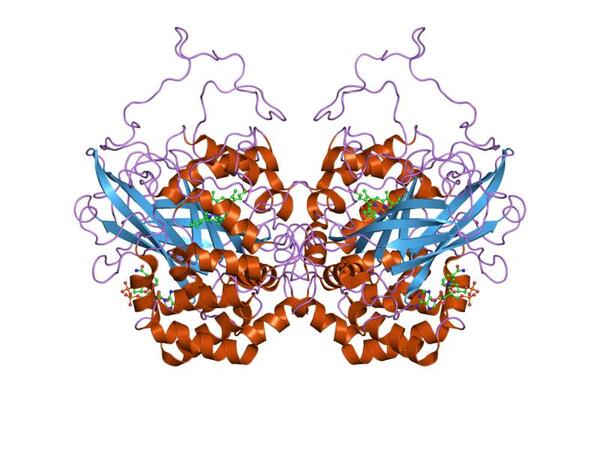
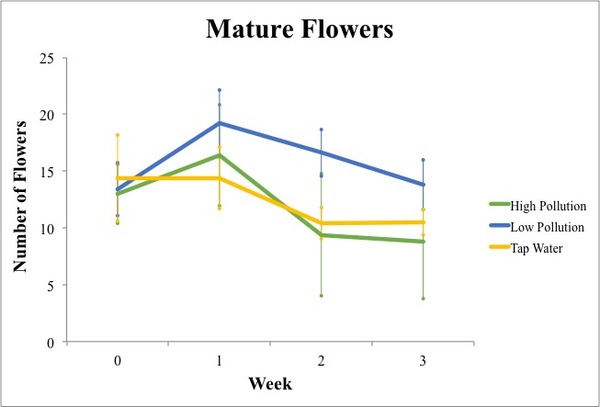
In a world where water shortage is becoming an increasing concern, and where population increase seems inevitable, food shortage is an overwhelming concern for many. In this paper, the authors aim to characterize a drought-resistant strain of A. thaliana, investigating the cause for its water resistance. These and similar studies help us learn how plants could be engineered to improve their ability to flourish in a changing climate.
Read More...