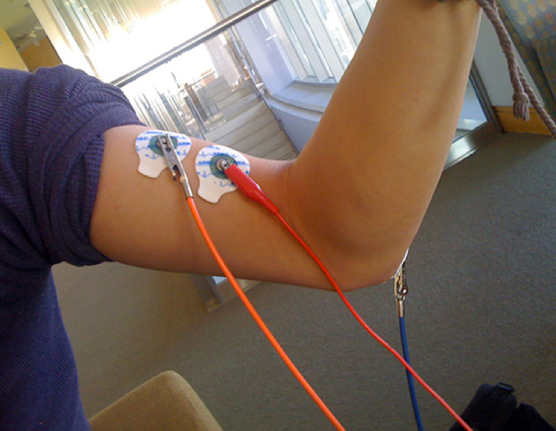
Control of voluntary and involuntary movements is one of the most important aspects of human neurological function, but the mechanisms of motor control are not completely understood. In this study, the authors use transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to stimulate a portion of the motor cortex while subjects performed either discrete (e.g. throwing) or rhythmic (e.g. walking) movements. By recording electrical activity in the muscles during this process, the authors showed that motor evoked potentials (MEPs) measured in the muscles during TMS stimulation are larger in amplitude for discrete movements than for rhythmic movements. Interestingly, they also found that MEPs during transitions between rhythmic and discrete movements were nearly identical and larger in amplitude than those recorded during either rhythmic or discrete movements. This research provides important insights into the mechanisms of neurological control of movement and will serve as the foundation for future studies to learn more about temporal variability in neural activity during different movement types.
Read More...
_resized.jpg)