
The authors investigate various methods to decrease heart rate after drinking caffeine.
Read More...Decreasing heart rate after consuming caffeine

The authors investigate various methods to decrease heart rate after drinking caffeine.
Read More...The non-nutritive sweeteners acesulfame potassium and neotame slow the regeneration rate of planaria
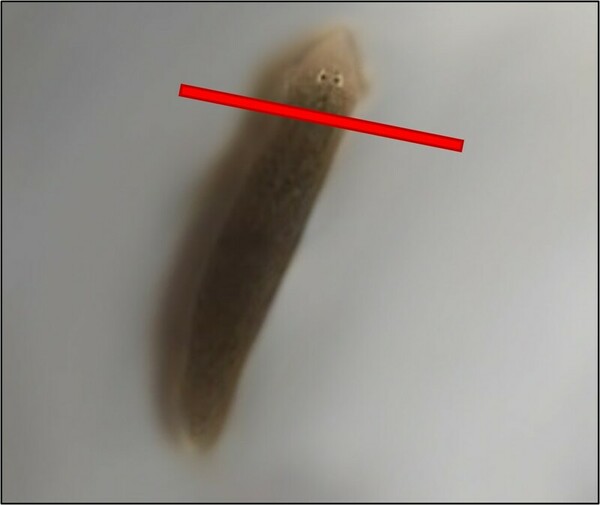

The consumption of sugar substitute non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS) has dramatically increased in recent years. Despite being advertised as a healthy alternative, NNS have been linked to adverse effects on the body, such as neurodegenerative diseases (NDs). In NDs, neural stem cell function is impaired, which inhibits neuron regeneration. The purpose of this study was to determine if the NNS acesulfame potassium (Ace-K) and neotame affect planaria neuron regeneration rates. Since human neurons may regenerate, planaria, organisms with extensive regenerative capabilities due to stem cells called neoblasts, were used as the model organism. The heads of planaria exposed to either a control or non-toxic concentrations of NNS were amputated. The posterior regions of the planaria were observed every 24 hours to see the following regeneration stages: (1) wound healing, (2) blastema development, (3) growth, and (4) differentiation. The authors hypothesized that exposure to the NNS would slow planaria regeneration rates. The time it took for the planaria in the Ace-K group and the neotame group to reach the second, third, and fourth regeneration stage was significantly greater than that of the control. The results of this study indicated that exposure to the NNS significantly slowed regeneration rates in planaria. This suggests that the NNS may adversely impact neoblast proliferation rates in planaria, implying that it could impair neural stem cell proliferation in humans, which plays a role in NDs. This study may provide insight into the connection between NNS, human neuron regeneration, and NDs.
Read More...Testing Simarouba amara’s therapeutic effects against weedicide-induced tumor-like morphology in planarians
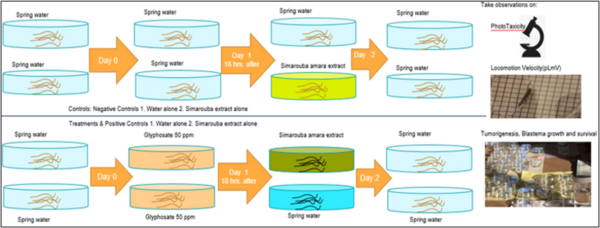
According to the World Health Organization, cancer is a leading cause of death globally. The disease’s prevalence is rapidly increasing in association with factors including the increased use of pesticides and herbicides, such as glyphosate, which is one of the most widely used herbicide ingredients. Natural antioxidants and phytochemicals are being tested as anti-cancer agents due to their antiproliferative, antioxidative, and pro-apoptotic properties. Thus, we aimed to investigate the potential role of S. amara extract as a therapeutic agent against glyphosate-induced toxicity and tumor-like morphologies in regenerating and homeostatic planaria (Dugesia dorotocephala).
Read More...Innovative Treatment for Reducing Senescence and Revitalizing Aging Cells through Gene Silencing
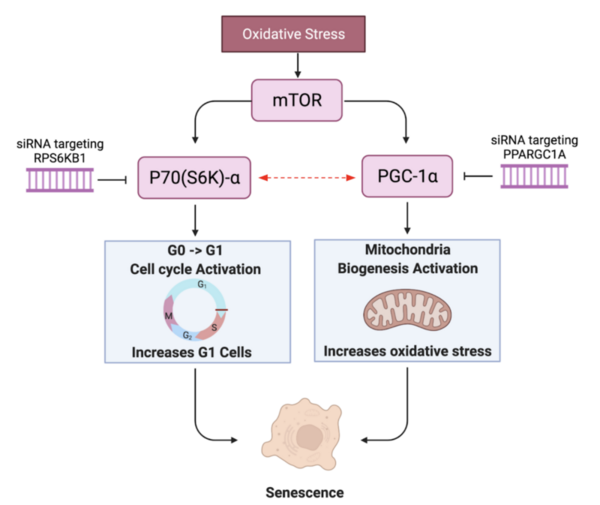
Cellular senescence plays a key role in aging cells and is attributed to a number of disease and pathology. These authors find that genetic editing of both RPS6KB1 and PPARGC1A revitalizes a human skin fibroblast cell line.
Read More...Varying Growth Hormone Levels in Chondrocytes Increases Proliferation Rate and Collagen Production by a Direct Pathway

Bennett and Joykutty test whether growth hormone directly or indirectly affected the rate at which cartilage renewed itself. Growth hormone could exert a direct effect on cartilage or chondrocytes by modifying the expression of different genes, whereas an indirect effect would come from growth hormone stimulating insulin-like growth factor. The results from this research support the hypothesis that growth hormone increases proliferation rate using the direct pathway. This research can be used in the medical sciences for people who suffer from joint damage and other cartilage-related diseases, since the results demonstrated conditions that lead to increased proliferation of chondrocytes. These combined results could be applied in a clinical setting with the goal of allowing patient cartilage to renew itself at a faster pace, therefore keeping those patients out of pain from these chondrocyte-related diseases.
Read More...The Clinical Accuracy of Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring for ex vivo Artificial Pancreas
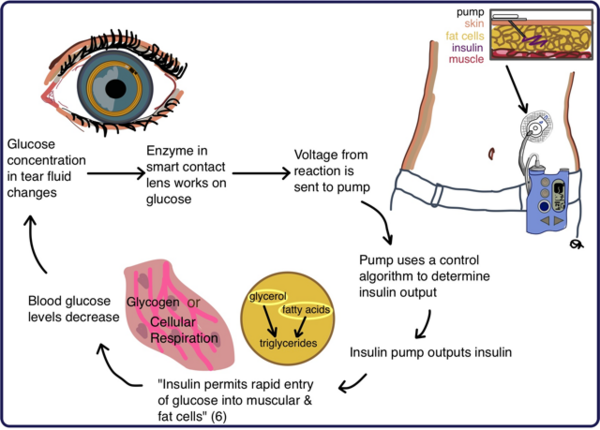
Diabetes is a serious worldwide epidemic that affects a growing portion of the population. While the most common method for testing blood glucose levels involves finger pricking, it is painful and inconvenient for patients. The authors test a non-invasive method to measure glucose levels from diabetic patients, and investigate whether the method is clinically accurate and universally applicable.
Read More...Lung cancer AI-based diagnosis through multi-modal integration of clinical and imaging data
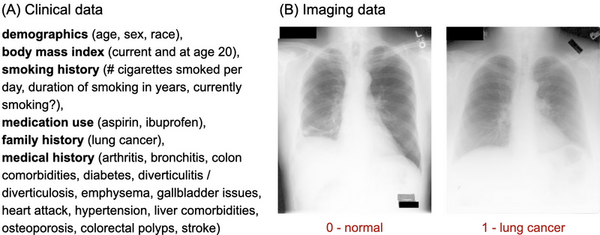
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...Reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein: An eight-week, open-label clinical trial of three oral supplements
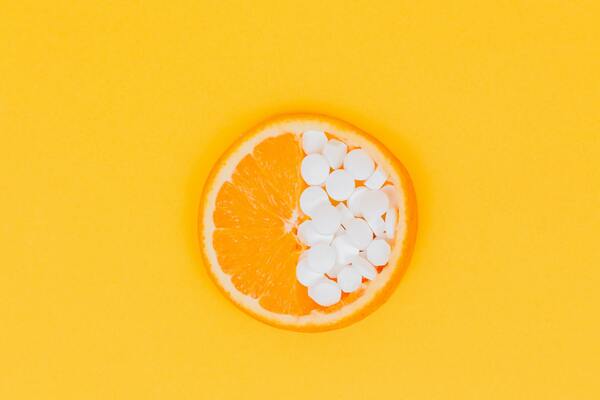

In this study, the effects of vitamin C, ginger, or curcumin supplements on C-reactive protein levels in healthy participants are determined in an eight-week open-label trial.
Read More...Culturally Adapted Assessment Tool for Autism Spectrum Disorder and its Clinical Significance
Diagnosing of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) using tools developed in the West is challenging in the Indian setting due to a huge diversity in sociocultural and economic backgrounds. Here, the authors developed a home-based, audiovisual game app (Autest) suitable for ASD risk assessment in Indian children under 10 years of age. Ratings suggested that the tool is effective and can reduce social inhibition and facilitate assessment. Further usage and development of Autest can improve risk assessment and early intervention measures for children with ASD in India.
Read More...A comparison of use of the mobile electronic health record by medical providers based on clinical setting

The electronic health record (EHR), along with its mobile application, has demonstrated the ability to improve the efficiency and accuracy of health care delivery. This study included data from 874 health care providers over a 12-month period regarding their usage of mobile phone (EPIC® Haiku) and tablet (EPIC® Canto) mEHR. Ambulatory and inpatient care providers had the greatest usage levels over the 12-month period. Awareness of workflow allows for optimization of mEHR design and implementation, which should increase mEHR adoption and usage, leading to better health outcomes for patients.
Read More...