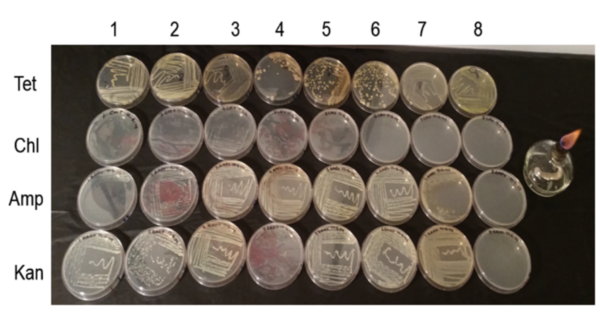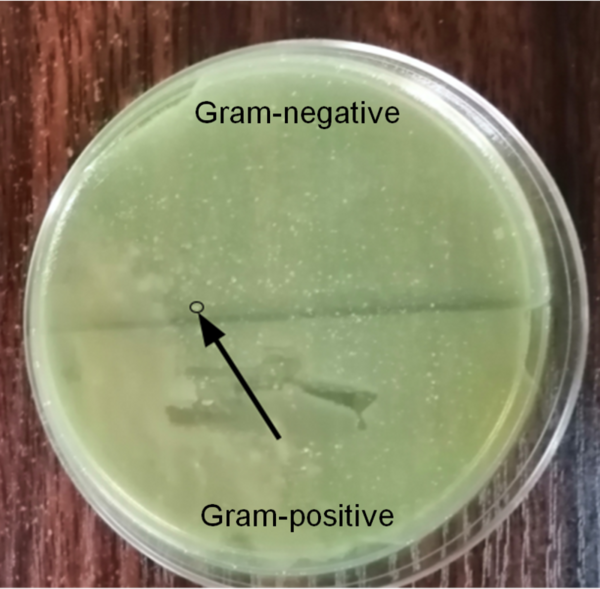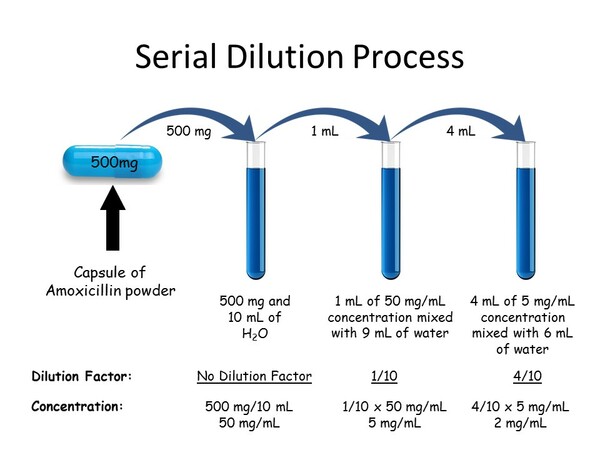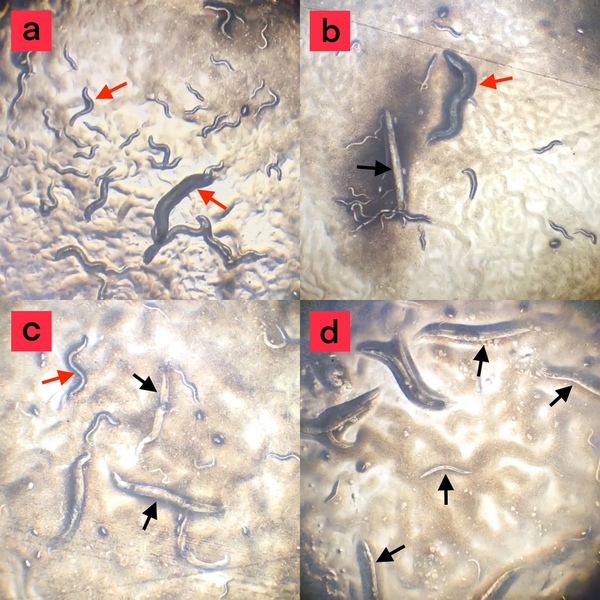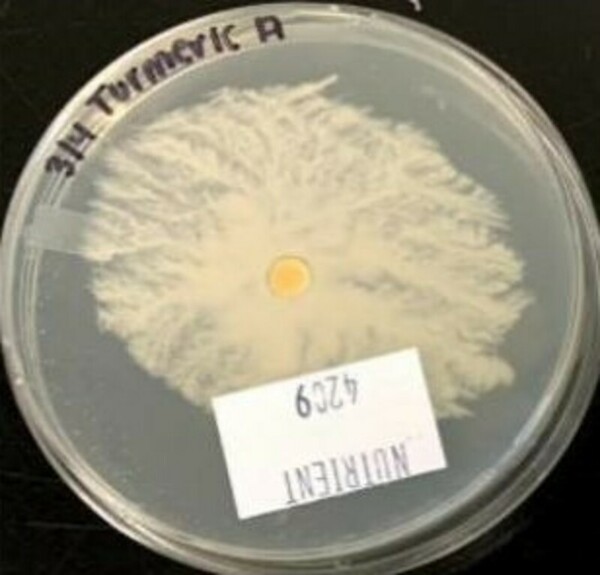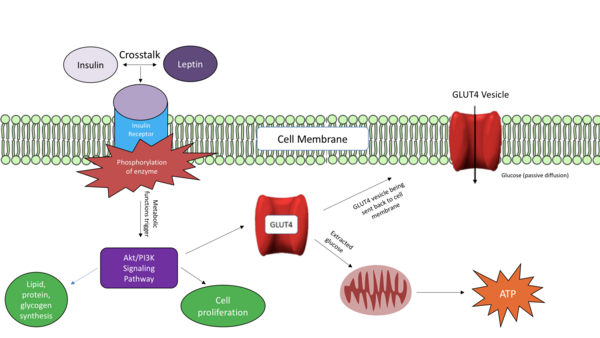
A primary cause of diabetes is insulin resistance, which is caused by disruption of insulin signal transduction. The objective of this study was to maximize insulin sensitivity by creating a more effective, early intervention-based treatment to avert severe T2D. This treatment combined metformin, “the insulin sensitizer”, and medicinal plants, curcumin, fenugreek, and nettle.
Read More...