In this article, the authors propose an effective, environmentally-friendly method of producing conductive ink using expired waste oil, polystyrene, and graphene.
Read More...Environmentally-friendly graphene conductive ink using graphene powder, polystyrene, and waste oil

In this article, the authors propose an effective, environmentally-friendly method of producing conductive ink using expired waste oil, polystyrene, and graphene.
Read More...A Juxtaposition of Airborne Microplastics and Fiber Contamination in Various Environments
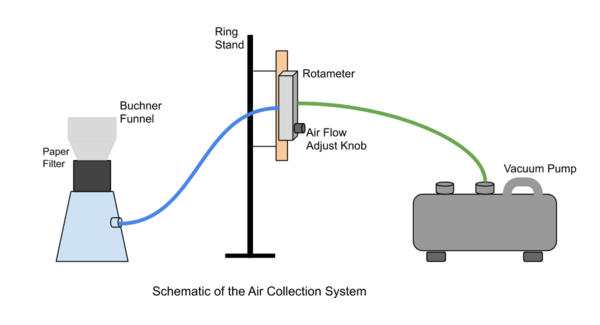
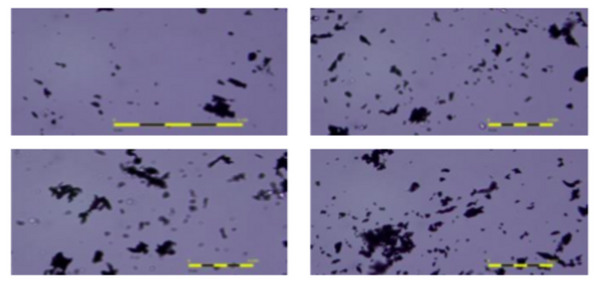
Microplastics can have detrimental effects on various wildlife, as well as pollute aquatic and atmospheric environments. This study focused on air samples collected from five locations to investigate microplastic concentrations in atmospheric fallout from indoor and outdoor settings, through a process utilizing a hand-held vacuum pump and a rotameter. The authors found that the difference between the average number of microplastic fragments and fibers collected from all locations was not large enough to be statistically significant. The results collected in this study will contribute to knowledge of the prevalence of airborne microplastics.
Read More...What is the optimal fuel for space flight? Efficiency, cost, and environmental impact

Here, the authors sought to investigate the efficiency, cost, and environmental impact of several possible propellants that are or could be used for space flight. By deriving three novel equations, they identified harm, energy, and cost scores for each fuel, suggesting that considering each factor will be essential to the ongoing growth of the space industry.
Read More...Novel environmentally friendly approach to wastewater treatment eliminates aluminum sulfate and chlorination

The authors tested environmentally-friendly alternatives to wastewater treatment chemicals, including activated charcoal for filtration and citrus peels for preventing bacterial growth.
Read More...Low environmental pH inhibits phagosome formation and motility of Tetrahymena pyriformis
.jpg)
In this study, the authors look into some of the implications of rising carbon dioxide levels by studying the effects of acidic pH on the ability of T. pyriformis to feed by quantifying phagosome formation and motility.
Read More...Effect of environment factors on the expression of soluble PDE8A1 in E. coli
PDE8, a type of phosphodiesterase (PDE), is proven to be crucial in various cellular activities and physiological activities by influencing second messenger systems. It is involved in a wide range of diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease and various heart diseases. However, there is limited information about PDE8 selective inhibitors. This work aimed to improve the solubility and yield of PDE8 in the supernatant by exploring suitable culture conditions, including temperatures and different additives.
Read More...Role of Environmental Conditions on Drying of Paint
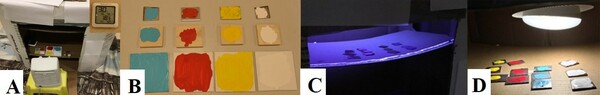
Reducing paint drying time is an important step in improving production efficiency and reducing costs. The authors hypothesized that decreased humidity would lead to faster drying, ultraviolet (UV) light exposure would not affect the paint colors differently, white light exposure would allow for longer wavelength colors to dry at a faster rate than shorter wavelength colors, and substrates with higher roughness would dry slower. Experiments showed that trials under high humidity dried slightly faster than trials under low humidity, contrary to the hypothesis. Overall, the paint drying process is very much dependent on its surrounding environment, and optimizing the drying process requires a thorough understanding of the environmental factors and their interactive effects with the paint constituents.
Read More...Effect of environmental factors on bacterial flora of normal human skin
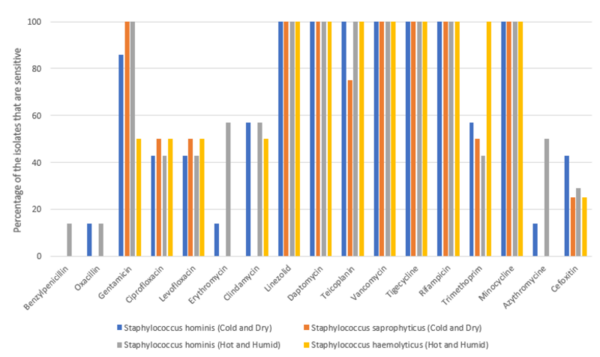
The authors looked how different working conditions impacted the microbiome of the human skin.
Read More...The impact of environmental noise on the cognitive functions and mental workload of high school students
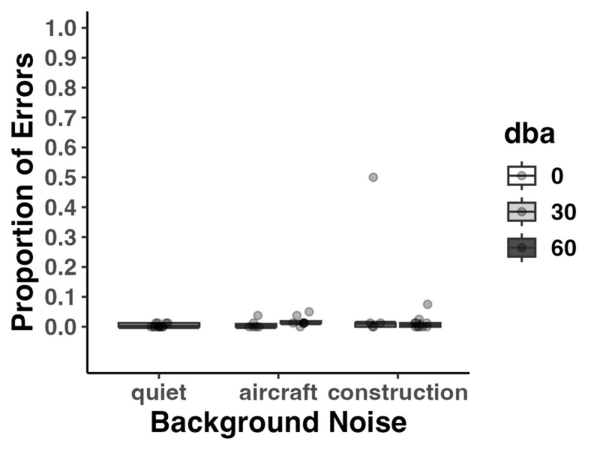
Authors examine the impact of environmental noise on cognitive processes in teenagers, focusing on five different noise conditions: two types of noise (aircraft and construction) at two different decibel levels (30 dBA and 60 dBA) and a quiet condition.
Read More...Impact of environmental stressors on ultrasonic acoustic emissions in different species of plants
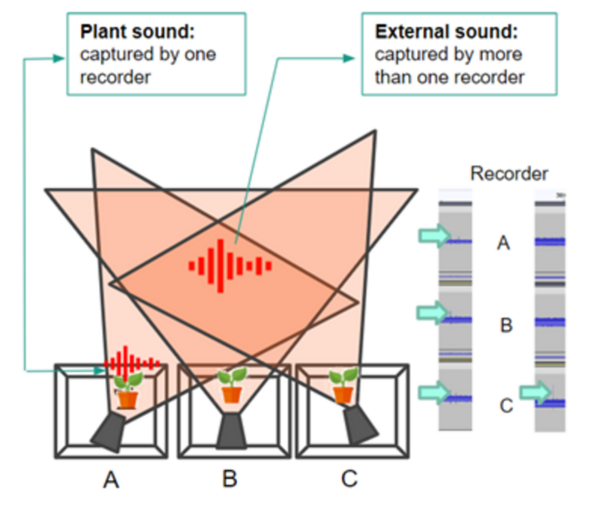
Current horticulture practices often rely on pesticides, causing environmental harm. To address this, authors explore the use of ultrasonic sound emissions to detect plant stress at an individual level.
Read More...