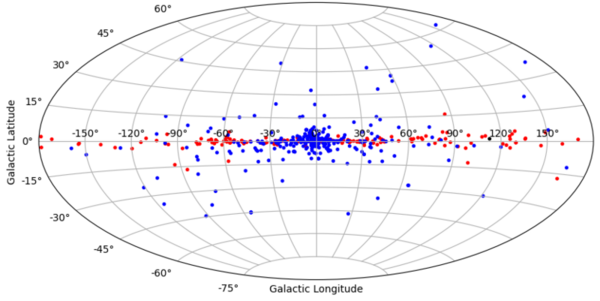
The authors looked at variables and their patterns and how those contribute to the properties of X-ray binaries.
Read More...Analysis of quantitative classification and properties of X-ray binary systems

The authors looked at variables and their patterns and how those contribute to the properties of X-ray binaries.
Read More...The journey to Proxima Centauri b
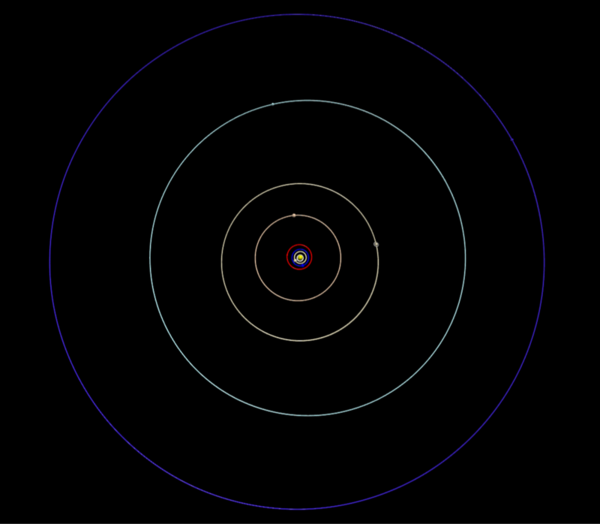
Someday, rockets from Earth may be launched towards worlds beyond our solar system. But will these rockets be able to reach their destination within a human lifetime? Ramaswamy and Giovinazzi simulate rocket launches to an Earth-like exoplanet to uncover whether it's physically possible to complete the journey within a lifetime.
Read More...Determining the Habitable Zone Around a Star
Life requires many things, including a hospitable temperature, elements, and energy. Here the authors utilize Newton's laws of physics and information relating a star's luminosity and temperature to determine the minimum and maximum masses and luminosities of planets and stars that would support life as we know it. This work can be used to determine the likelihood of a planet being able to support life based on attributes we can measure from here on Earth.
Read More...Defying chemical tagging: inhomogeneities in the wide binary system HIP 34407/HIP 34426

This assessed the hypothesis that stars in wide binary systems are chemically homogeneous because of their shared origin. Abundances of the HIP 34407/HIP 34426 binary were obtained by analyzing high-resolution spectra of the system. Discrepancies found in the system’s elemental abundances might be an indicator of the presence of rocky planets around this star. Thus, the differences found in chemical composition might demonstrate limitations in the assumptions of chemical tagging.
Read More...Differentiating characteristics in exoplanet host stars

The authors looked at what conditions with host stars favor development of exoplanets.
Read More...Photometric analysis of Type Ia Supernova 2023jvj

Here the authors conducted a photometric analysis of Supernova (SN) 20234jvj. Through generating a light curve, they determined SN 2023jvj to be a Type Ia supernova located approximately 1.246e8 parasecs away from Earth.
Read More...Color photometry and light curve modeling of apparent transient 2023jri
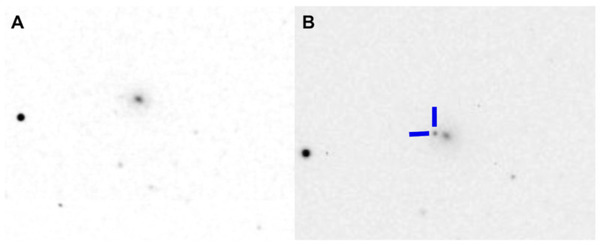
Observing transients like supernovae, which have short-lived brightness variations, helps astronomers understand cosmic phenomena. This study analyzed transient 2023jri, hypothesizing it was a Type IIb supernova. By collecting and analyzing data over four weeks, including light and color curves, they confirmed its classification and provided additional insights into this less-studied supernova type.
Read More...Photometric analysis and light curve modeling of apparent transient 2020pni

Supernovas are powerful explosions that result from gravitational collapse of a massive star. Using photometric analysis Arora et al. set out to investigate whether 2020pni (located in galaxy UGC 9684) was a supernova. They were ultimately able to identify 2020pni as a Type II-L supernova and determine it's distance from earth.
Read More...Comparing Measurements of Sun-Earth Distance: Shadow Method and Two Pinhole Method Variations
This study compares three methods regarding their accuracy in calculating the distance between the Earth and the Sun. The hypothesis presented was that the shadow method would have the greatest mean accuracy, followed by the tube pinhole method, and finally the plate pinhole method. The results validate the hypothesis; however, further investigation would be helpful in determining effective mitigation of each method’s limitations and the effectiveness of each method in determining the distance of other light-emitting objects distant from the Earth.
Read More...Exploring the Wonders of the Early Universe: Green Pea Galaxies and Light Flux

Studying other galaxies can help us understand the origins of the universe. Here, the authors study a type of galaxies known as Green Peas gaining insights that could help inform our understanding of Lyman alpha emitters, one of the first types of galaxies that existed in the early universe.
Read More...