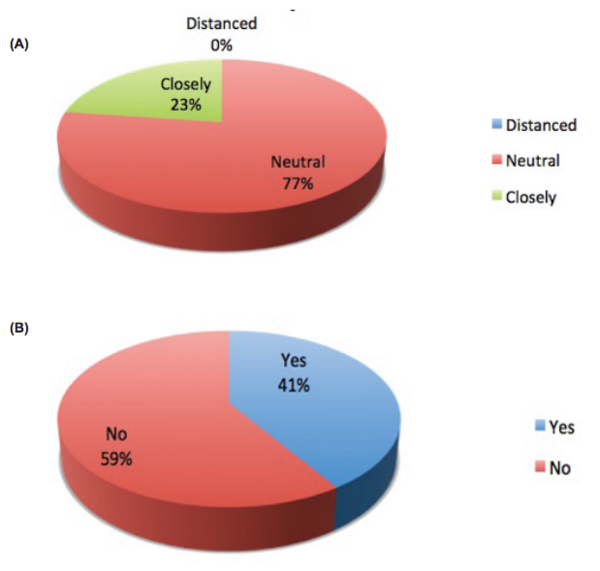
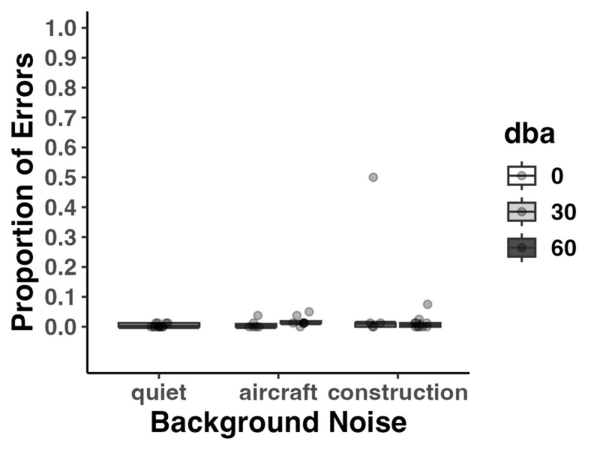
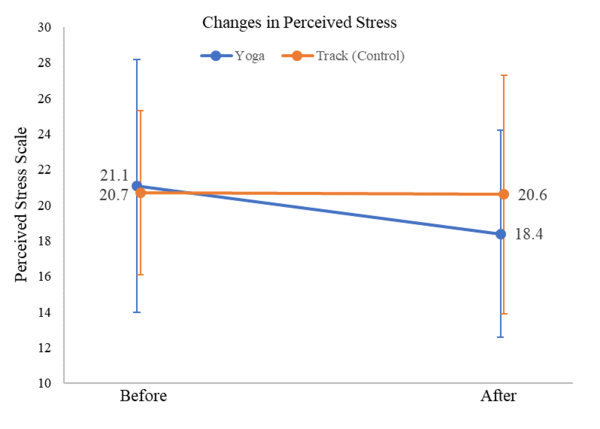
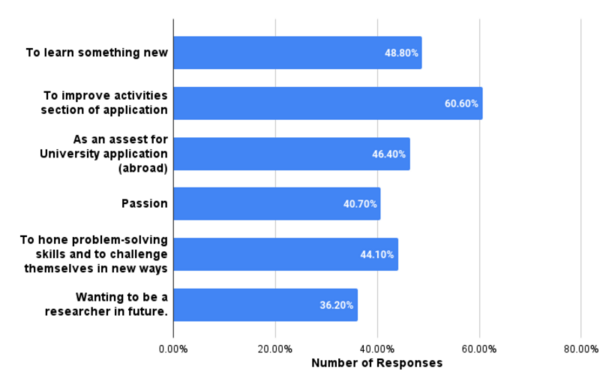
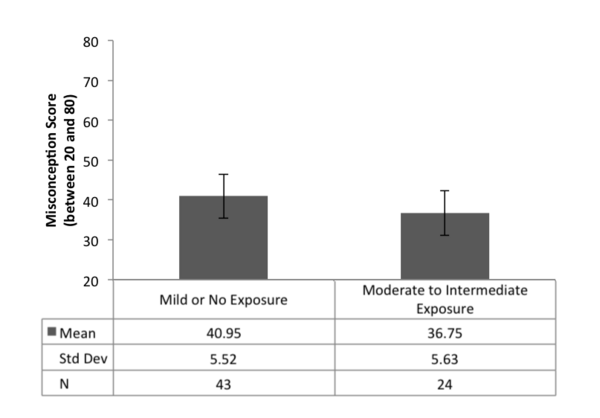
Microplastics (MPs) are inorganic material that have been observed within items destined for human consumption, including water, and may pose a potential health hazard. Here we estimated the average amount of MPs junior high students and teachers consumed from different water sources and determined whether promoting awareness of microplastic (MP) exposure influenced choice of water source and potential MPs consumed.
Read More...