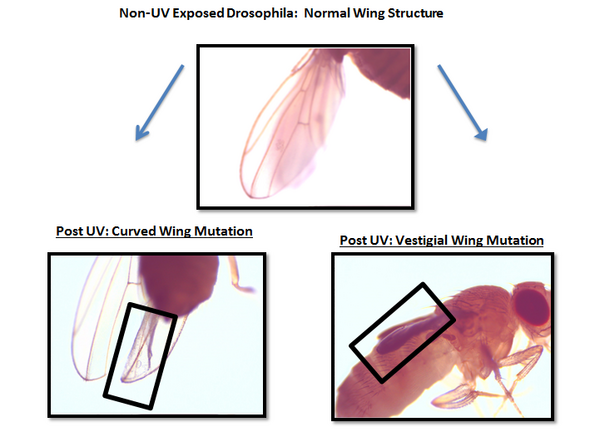
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is known to alter DNA structure and impair cellular function in all living organisms. In this study, Lateef et al examine the effects of UV radiation to determine whether antioxidant-enriched nutrition can combat the potential deleterious effects of UV radiation on Drosophila melanogaster. They found that UVB (320nm) radiation caused a 59% decrease in the Drosophila lifespan and mutagenic effects on flies' physical appearance, but did not significantly affect fertility. Curcumin significantly prolonged lifespan and enhanced fertility for both UV- and non-UV-exposed flies. The research demonstrates the positive potential of natural antioxidants as weapons against radiation-induced diseases including cancer.
Read More...